1.手写 开发servlet步骤:
1.在tomcat中新建一个web应用,然后在web应用中新建一个WEB-INF/classes目录。2.在classes目录中新建一个FirstServlet:
package cn.itcast;import java.io.*;
import javax.servlet.*;public class FirstServlet extends GenericServlet
{public void service(ServletRequest req,ServletResponse res)throws ServletException,java.io.IOException{OutputStream out = res.getOutputStream();out.write("hello servlet!".getBytes());}
}3.set classpath=%classpath%;C:\apache-tomcat-8.5.4\lib\servlet-api.jar,然后编译servlet。4.在WEB-INF中新建web.xml文件,配置servlet对外访问路径。<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaeehttp://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd"version="3.1"><servlet><servlet-name>FirstServlet</servlet-name><servlet-class>cn.itcast.FirstServlet</servlet-class></servlet><servlet-mapping><servlet-name>FirstServlet</servlet-name><url-pattern>/FirstServlet</url-pattern></servlet-mapping></web-app>5.启动tomcat,ie访问。
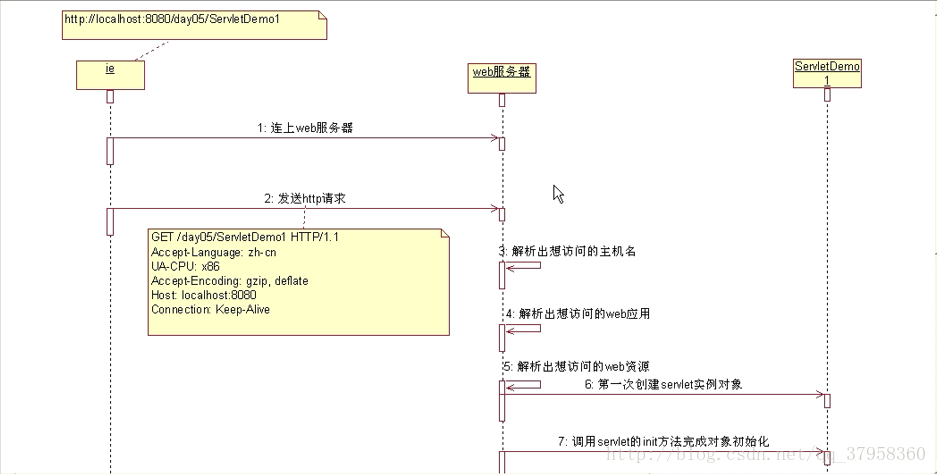
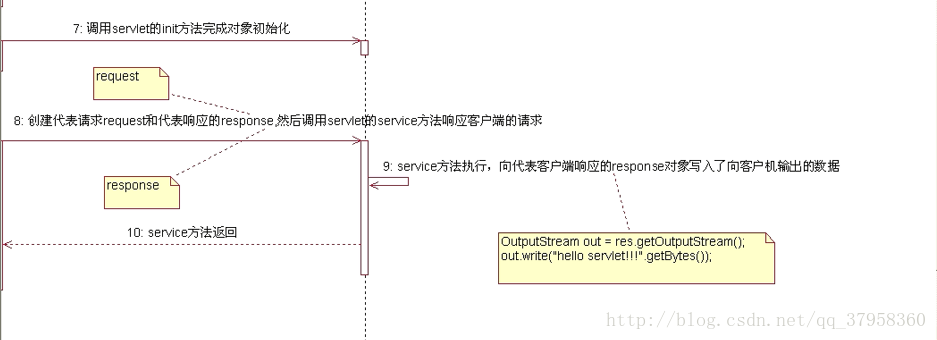
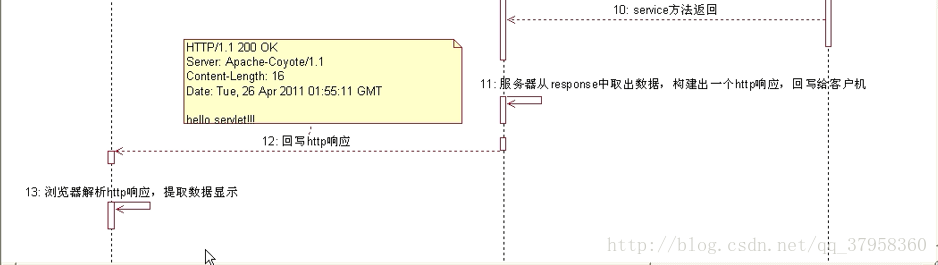
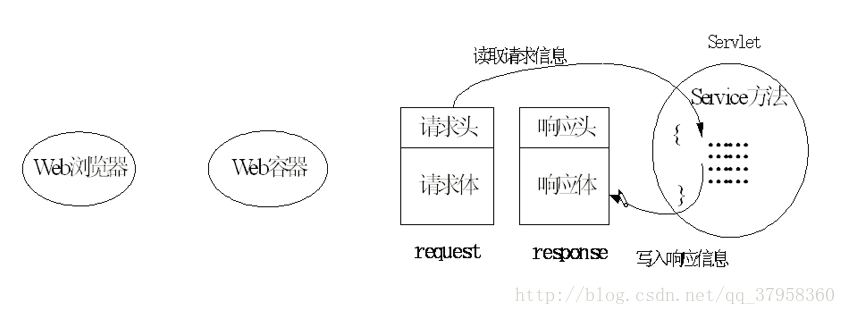
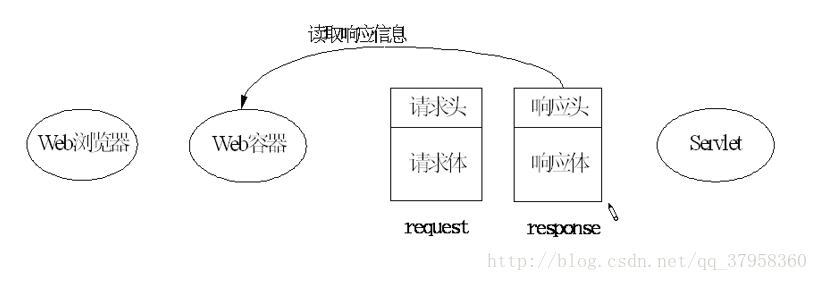
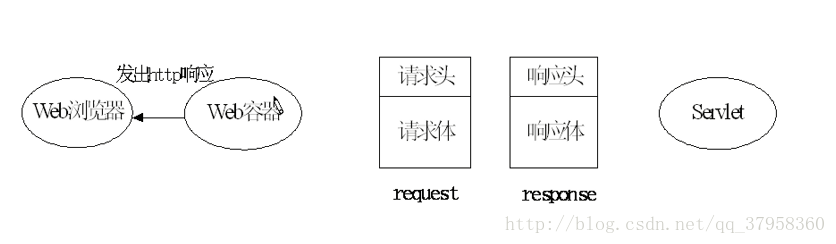
2.servlet的调用过程 和 生命周期:
servlet 的生命周期:
servlet对象在用户第一次访问的时候创建,生命周期开始。然后init方法会执行对象初始化。servlet对象一直驻留在内存中响应后续的请求。客户端的每次请求会执行service方法。servlet被摧毁的时候destroy方法会被执行。web服务器停止或者wen应用被删除的时候,servlet会被摧毁,生命周期结束。servlet运行过程:
2.使用Eclipse开发servlet
①Servlet接口的实现类:HttpServlet3.Servlet开发的一些重要细节:
①servlet的映射
②servlet的多映射
③servlet的多映射的通配符细节
④Servlet对象在客户端访问web服务器时创建一次,init方法只调用一次
⑤在web应用的web.xml元素配置,对象就在web服务器启动时就创建。
⑥tomcat服务器有自己配置缺省servlet
⑦多个客户端并发访问一个servlet时容易发生线程安全问题
4.web服务器会给servlet多个对象:
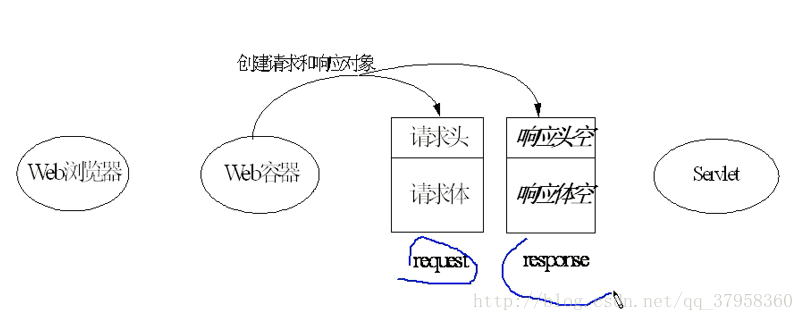
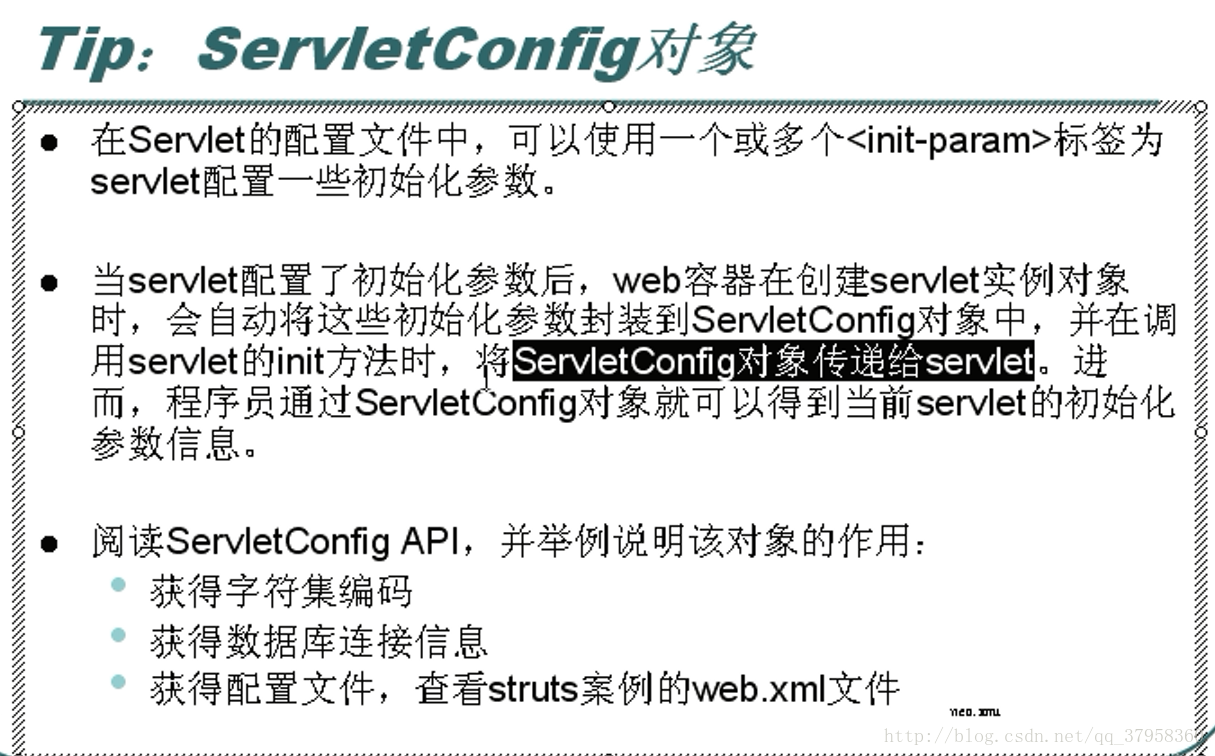
ServletConfig,ServletContext,request,response,Cookie,Session。等等5.ServletConfig对象:在web应用的配置文件web.xml中配置必要的数据。
配置:
获取:
6.ServletContext对象:
ServletContext方法的应用:
context域对象(request域,session域,page域)
①setAttribute(),getAttribute():实现servlet之间的数据共享:
/*ServletContext域:1.这时一个容器2.servletcontext域这句话说明了这个容器作用范围,也就是应用程序范围。*/
//通过servletcontext实现Demo4和Demo5的数据共享
public class ServletDemo4 extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)throws ServletException, IOException {String data = "aaa";this.getServletContext().setAttribute("data", data);}public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)throws ServletException, IOException {doGet(request, response);}}public class ServletDemo5 extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)throws ServletException, IOException {String value = (String)this.getServletContext().getAttribute("data");System.out.println(value);}public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)throws ServletException, IOException {doGet(request, response);}}
②获取web应用的初始化参数
web.xml:<context-param><param-name>data</param-name><param-value>xxxx</param-value></context-param>//获取web应用的初始化参数
public class ServletDemo6 extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)throws ServletException, IOException {this.getServletContext().getInitParameter("data");}public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)throws ServletException, IOException {doGet(request, response);}}③实现servlet转发:servlet不适合做数据输出,转发给JSP处理。
转发:帮你找别人处理请求,客户端请求一次
重定向:告诉你该找谁重发请求,客户端请求两次。
如果用servletcontext带数据来转发,可能会出现多个servlet对象覆盖原有的数据的安全问题:
//通过ServletContext实现请求转发public class ServletDemo6 extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)throws ServletException, IOException {String data = "abacsbd";//数据带给1.jsp(不能通过context域,要通过request域)this.getServletContext().setAttribute("data", data);//转发对象:RequestDispatcher rd = this.getServletContext().getRequestDispatcher("/1.jsp");rd.forward(request, response);}public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)throws ServletException, IOException {doGet(request, response);}}1.jsp:<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"><html><head><title>My JSP '1.jsp' starting page</title></head><body><font color="red"> <%String data = (String) application.getAttribute("data");out.write(data);%></font></body>
</html>④:利用ServletContext对象读取资源文件
得到文件路径
读取资源文件的三种方式
.properties文件
ServletContext对象生命周期:web服务器启动时产生,有多少个应用,就有多少个ServletContext对象。停止服务器或者移除web应用,则ServletContext对象被销毁。
//通过servletcontext读取资源文件
public class ServletDemo7 extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)throws ServletException, IOException {
// test1(); //标准方式test2(); //传统方式}//读取资源文件,注意问题:一般不用传统方式去读取,相对路径问题,传统方式读的相对路径是jvm,即tomcat的启动目录。private void test2() throws IOException {//获取绝对路径(好处是 可以获得资源的名称,下载的时候需要)String path = this.getServletContext().getRealPath("/WEB-INF/classes/db.properties");String filename = path.substring(path.lastIndexOf("\\")+1);System.out.println(filename);//这个时候可以用传统方式读取FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(path);Properties props = new Properties();props.load(in);String url = props.getProperty("url");String username = props.getProperty("username");String password = props.getProperty("password");System.out.println(url);}public void test1() throws IOException {InputStream in = this.getServletContext().getResourceAsStream("/WEB-INF/classes/db.properties");Properties props = new Properties();props.load(in);String url = props.getProperty("url");String username = props.getProperty("username");String password = props.getProperty("password");System.out.println(url);}public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)throws ServletException, IOException {doGet(request, response);}}处理数据一般放在dao包里:
web应用中的普通Java程序如何读取资源文件。
//Servlet调用其他其他程序,在其他程序中如何读取资源文件(通过类加载器)
public class ServletDemo8 extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)throws ServletException, IOException {UserDao dao = new UserDao();dao.update();}public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)throws ServletException, IOException {doGet(request, response);}}//如果读取资源文件的程序部是servlet的话,就只能通过类装载器去读了。//①文件不能太大
//②类装载器只装再一次,所以装载一次后不再装载,即使后来对资源有改动//②的解决办法:获取绝对路径,传统方法读取public class UserDao {
/* private static Properties dbconfig = new Properties();static {// 得到类的加载器try{ClassLoader cl= UserDao.class.getClassLoader();InputStream in = cl.getResourceAsStream("db.properties");dbconfig.load(in);}catch(Exception e){throw new ExceptionInInitializerError(e);}}*///通过类装载的方式得到资源文件的位置,再通过传统方式读取资源文件的数据,这样可以读取到更新后的数据。public void update() throws IOException {/* //以下代码虽然可以读取资源文件的的数据,但是无法获取更新后的数据。String url = dbconfig.getProperty("url");String username = dbconfig.getProperty("username");String password = dbconfig.getProperty("password");System.out.println(url);*/String path = UserDao.class.getClassLoader().getResource("db.properties").getPath();FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(path);Properties dbconfig = new Properties();dbconfig.load(in);System.out.println(dbconfig.getProperty("url"));}public void find(){}
}