目录
- 各组件深入之Spring Cloud Eureka
-
- **Eureka Server**
- **Eureka Client**
- **Eureka Server的自我保护机制**
- 服务发现原理
- Eureka Client 源码解析
-
- 读取自身配置信息
- 服务发现客户端
- 拉取注册表信息
-
- 全量拉去注册表信息
- 增量拉取注册表信息
- 服务注册
- 初始化定时任务
-
- 缓存刷新定时任务与发送心跳定时任务
- 按需注册定时任务
- 服务下线
- Eureka Server源码解析
-
- 服务实例注册表
- 服务注册
- 接受服务心跳
- 服务剔除
- 服务下线
- 集群同步
-
- Eureka Server初始化本地注册表信息
- Eureka Server之间注册表信息的同步复制
- 获取注册表中服务实例信息
-
- getApplicationsFromMultipleRegions获取全量注册表数据
- getApplicationDeltasFromMultipleRegions从多地区获取增量式注册表数据。
- **Eureka和ZooKeeper**
-
- **ZooKeeper保证CP**
- **Eureka保证AP**
在前面的文章中我们进行学习了Spring Cloud的使用,那么我们对各个组件的使用是不是还不够深入,那么从今天开始我们将逐一进行学习Spring Cloud Netflix中所提供的组件。今天我们现看下服务注册与发现Eureka。
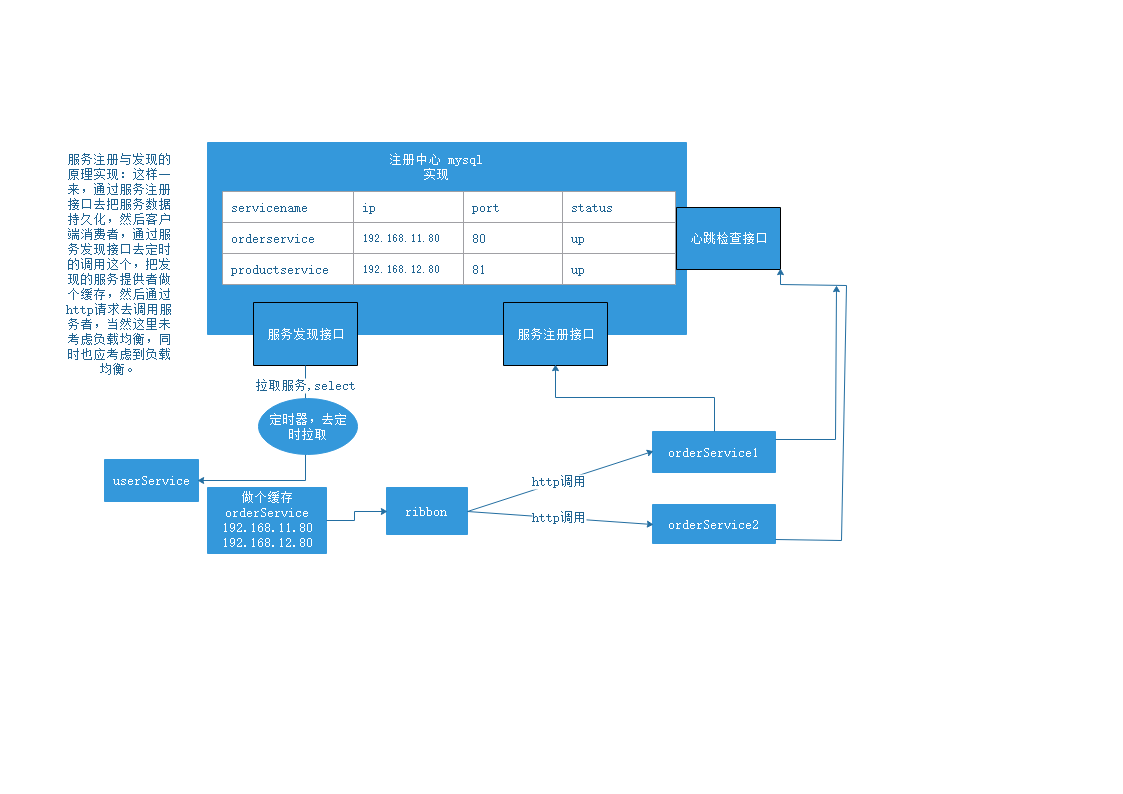
在看Eureka之前我们先看下简略版的服务注册与发现的机制
 ](https://imgchr.com/i/dO4A81)
](https://imgchr.com/i/dO4A81)
这个思路是把所有的服务的状态用数据库给保存起来,通过三个接口进行完成。一个是服务发现接口,一个是服务注册接口,一个是心跳检测接口,
服务发现接口:客户端调用时通过这个接口时,去数据库中查询到这个服务的状态,
服务注册接口:当服务提供者进行发布时通过服务注册接口进行把服务信息保存到数据库中,供服务发现接口调用。
心跳检测接口:定时的检测服务是否可用,不可用时将信息告诉服务提供者,令其再次发布,更新数据库中的服务状态。
当服务进行发布的时候通过服务注册接口去把服务信息持久话到数据库,客服端消费者通过服务发现接口去定时的取数据库中查询,看看服务提供者是否在线。如果在线则进行调用,在服务提供者通过服务注册接口去保存数据库的同时,需要调用心跳检查接口,如果掉线从新写入数据库,更改其状态。
各组件深入之Spring Cloud Eureka
通常来说服务注册与发现包括两部分,一个是服务器端,另一个是客户端。Server是一个公共服务,为Client提供服务注册和发现的功能,维护注册到自身的Client的相关信息,同时提供接口给Client获取注册表中其他服务的信息,使得动态变化的Client能够进行服务间的相互调用。Client将自己的服务信息通过一定的方式登记到Server上,并在正常范围内维护自己信息一致性,方便其他服务发现自己,同时可以通过Server获取到自己依赖的其他服务信息,完成服务调用
Eureka是一项基于REST(代表性状态转移)的服务,主要在AWS云中用于查找服务,以实现负载均衡和中间层服务器的故障转移。 我们称此服务为Eureka服务器服务注册与发现。 Eureka还带有一个基于Java的客户端组件Eureka Client,它使与服务的交互变得更加容易。 客户端还具有一个内置的负载平衡器,可以执行基本的循环负载平衡。 Netflix使用更复杂的负载均衡器将Eureka包装起来,以基于流量,资源使用,错误条件等多种因素提供加权负载均衡,以提供出色的弹性.
原理:主管服务注册与发现,也就是微服务的名称注册到Eureka,就可以通过Eureka找到微服务,而不需要修改服务调用的配置文件。
分析:Spring Cloud封装了Netflix公司开发的Eureka模块来实现服务的注册与发现,采用的c-s的设计架构,Eureka Server作为服务注册功能的服务器,他是服务注册中心。而系统的其他微服务,使用Eureka的客户端连接到Eureka Server并维持心跳。这样系统的维护人员可以通过Eureka Server来监控系统中的各个微服务是否正常运行。Spring Cloud的一些其他模块(比如Zuul)就可以通过Eureka Server来发现系统其他的微服务,并执行相关逻辑。
Eureka Server
Eureka Server提供服务注册服务,各个节点启动后,会在Eureka Server中进行注册, 这样Eureka Server中的服务注册表中将会存储所有可用服务节点的信息,服务节点的信息可以在界面中直观的看到。
Eureka Server既可以独立部署,也可以集群部署。在集群部署的情况下,Eureka Server间会进行注册表信息同步的操作,这时被同步注册表信息的Eureka Server将会被其他同步注册表信息的Eureka Server称为peer.
通常来讲,一个Eureka Server也是一个Eureka Client,它会尝试注册自己,所以需要至少一个注册中心的URL来定位对等点peer。如果不提供这样一个注册端点,注册中心也能工作,但是会在日志中打印无法向peer注册自己的信息。在独立(Standalone)Eureka Server的模式下,Eureka Server一般会关闭作为客户端注册自己的行为。Eureka Server与Eureka Client之间的联系主要通过心跳的方式实现。心跳(Heartbeat)即Eureka Client定时向Eureka Server汇报本服务实例当前的状态,维护本服务实例在注册表中租约的有效性。
Eureka Server需要随时维持最新的服务实例信息,所以在注册表中的每个服务实例都需要定期发送心跳到Server中以使自己的注册保持最新的状态(数据一般直接保存在内存中)。为了避免Eureka Client在每次服务间调用都向注册中心请求依赖服务实例的信息,Eureka Client将定时从Eureka Server中拉取注册表中的信息,并将这些信息缓存到本地,用于服务发现
Eureka Client
Eureka Client是一个Java客户端, 用于简化Eureka Server的交互,客户端同时也具备一个内置的、 使用轮询(round-robin)负载算法的负载均衡器。在应用启动后,将会向Eureka Server发送心跳(默认周期为30秒),以证明当前服务是可用状态 (30秒发送一次心跳更新租约。 如果客户端几次无法续签租约)。 如果Eureka Server在一定的时间(默认90秒)未收到客户端的心跳,Eureka Server将会从服务注册表中把这个服务节点移除。 任何区域的客户端都可以查找注册表信息(每30秒发生一次)以查找其服务(可能在任何区域)并进行远程调用。
DiscoveryClient来源于spring-cloud-client-discovery,是Spring Cloud中定义用来服务发现的公共接口,在Spring Cloud的各类服务发现组件中(如NetflixEureka或Consul)都有相应的实现。它提供从服务注册中心根据serviceId获取到对应服务实例信息的能力。当一个服务实例拥有DiscoveryClient的具体实现时,就可以从服务注册中心中发现其他的服务实例。在Eureka Client中注入DiscoveryClient,并从Eureka Server获取服务实例的信息
Eureka Server的自我保护机制
如果在15分钟内超过85%的节点都没有正常的心跳,那么Eureka就认为客户端与注册中心出现了网络故障,此时会出现以下几种情况:
- Eureka不再从注册列表中移除因为长时间没收到心跳而应该过期的服务
- Eureka仍然能够接受新服务的注册和查询请求,但是不会被同步到其它节点上(即保证当前节点依然可用)
- 当网络稳定时,当前实例新的注册信息会被同步到其它节点中
因此, Eureka可以很好的应对因网络故障导致部分节点失去联系的情况,而不会像ZooKeeper那样使整个注册服务瘫痪。
服务发现原理
Eureka最初设计的目的是AWS(亚马逊网络服务系统)中用于部署分布式系统,所以首先对AWS上的区域(Regin)和可用区(Availability Zone)进行简单的介绍。
区域:AWS根据地理位置把某个地区的基础设施服务集合称为一个区域,区域之间相对独立。在架构图上,us-east-1c、us-east-1d、us-east-1e表示AWS中的三个设施服务区域,这些区域中分别部署了一个Eureka集群。
可用区:AWS的每个区域都是由多个可用区组成的,而一个可用区一般都是由多个数据中心(简单理解成一个原子服务设施)组成的。可用区与可用区之间是相互独立的,有独立的网络和供电等,保证了应用程序的高可用性。在上述的架构图中,一个可用区中可能部署了多个Eureka,一个区域中有多个可用区,这些Eureka共同组成了一个Eureka集群。
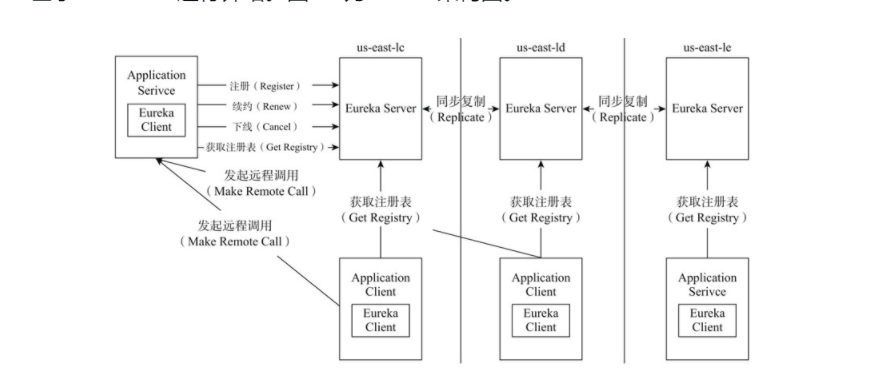
□ Application Service:是一个Eureka Client,扮演服务提供者的角色,提供业务服务,向Eureka Server注册和更新自己的信息,同时能从Eureka Server注册表中获取到其他服务的信息。
□ Eureka Server:扮演服务注册中心的角色,提供服务注册和发现的功能。每个Eureka Cient向Eureka Server注册自己的信息,也可以通过EurekaServer获取到其他服务的信息达到发现和调用其他服务的目的。
□ Application Client:是一个Eureka Client,扮演了服务消费者的角色,通过Eureka Server获取注册到其上其他服务的信息,从而根据信息找到所需的服务发起远程调用。
□ Replicate:Eureka Server之间注册表信息的同步复制,使Eureka Server集群中不同注册表中服务实例信息保持一致。
□ Make Remote Call:服务之间的远程调用。
□ Register:注册服务实例,Client端向Server端注册自身的元数据以供服务发现。
□ Renew:续约,通过发送心跳到Server以维持和更新注册表中服务实例元数据的有效性。当在一定时长内,Server没有收到Client的心跳信息,将默认服务下线,会把服务实例的信息从注册表中删除。
□ Cancel:服务下线,Client在关闭时主动向Server注销服务实例元数据,这时Client的服务实例数据将从Server的注册表中删除。
□ Get Registry:获取注册表,Client向Server请求注册表信息,用于服务发现,从而发起服务间远程调用。
Eureka Client 源码解析
Eureka Client为了简化开发人员的开发工作,将很多与Eureka Server交互的工作隐藏起来,自主完成。主要包含以下职能:
- 读取配置信息
- 服务发现客户端
- 拉取注册表信息
- 服务注册
- 初始化定时任务
- 服务下线

Eukeka Client通过Starter的方式引入依赖,Spring Boot将会为项目使用以下的自动配置类:
□ EurekaClientAutoConfiguration:Eureke Client自动配置类,负责EurekaClient中关键Beans的配置和初始化,如ApplicationInfoManager和EurekaClientConfig等。
□ RibbonEurekaAutoConfiguration:Ribbon负载均衡相关配置。
□ EurekaDiscoveryClientConfiguration:配置自动注册和应用的健康检查器。
读取自身配置信息
通过EurekaDiscoveryClientConfiguration配置类,Spring Boot帮助EurekaClient完成很多必要Bean的属性读取和配置,下表列出了EurekaDiscoveryClientConfiguration中的属性读取和配置类

Spring Cloud中的服务发现客户端DiscoveryClient进行进一步的介绍,它是客户端进行服务发现的核心接口.DiscoveryClient是Spring Cloud中用来进行服务发现的顶级接口,在Netflix Eureka或者Consul中都有相应的具体实现类
/**** Netflix Eureka or consul.ioDiscoveryClient是Spring Cloud中用来进行服务发现的顶级接口,在Netflix Eureka或者Consul中都有相应的具体实现类* @author Spencer Gibb*/
public interface DiscoveryClient {
/*** 获取实现类的描述* @return the description*/String description();/*** 通过服务Id获取服务实例的信息* @param serviceId the serviceId to query* @return a List of ServiceInstance*/List<ServiceInstance> getInstances(String serviceId);/*** 获取所有服务实例Id* @return all known service ids*/List<String> getServices();}
服务发现客户端
DiscoveryClient是Eureka Client的核心类,包括与Eureka Server交互的关键逻辑具备以下职能:
- 注册服务实例到Eureka Server中;
- 发送心跳更新与Eureka Server的租约;
- 在服务关闭时从Eureka Server中取消租约,服务下线;
- 查询在Eureka Server中注册的服务实例列表
EurekaDiscoveryClient实现了DiscoveryClient接口,但是通过查看EurekaDiscoveryClient中代码,会发现它是通过组合EurekaClien类实现接口的功能,如下为getInstance方法的实现:

public class EurekaDiscoveryClient implements DiscoveryClient {
public static final String DESCRIPTION = "Spring Cloud Eureka Discovery Client";private final EurekaInstanceConfig config;private final EurekaClient eurekaClient;public EurekaDiscoveryClient(EurekaInstanceConfig config, EurekaClient eurekaClient) {
this.config = config;this.eurekaClient = eurekaClient;}@Overridepublic String description() {
return DESCRIPTION;}@Overridepublic List<ServiceInstance> getInstances(String serviceId) {
List<InstanceInfo> infos = this.eurekaClient.getInstancesByVipAddress(serviceId,false);List<ServiceInstance> instances = new ArrayList<>();for (InstanceInfo info : infos) {
instances.add(new EurekaServiceInstance(info));}return instances;}public static class EurekaServiceInstance implements ServiceInstance {
private InstanceInfo instance;public EurekaServiceInstance(InstanceInfo instance) {
Assert.notNull(instance, "Service instance required");this.instance = instance;}public InstanceInfo getInstanceInfo() {
return instance;}@Overridepublic String getServiceId() {
return this.instance.getAppName();}@Overridepublic String getHost() {
return this.instance.getHostName();}@Overridepublic int getPort() {
if (isSecure()) {
return this.instance.getSecurePort();}return this.instance.getPort();}@Overridepublic boolean isSecure() {
// assume if secure is enabled, that is the defaultreturn this.instance.isPortEnabled(SECURE);}@Overridepublic URI getUri() {
return DefaultServiceInstance.getUri(this);}@Overridepublic Map<String, String> getMetadata() {
return this.instance.getMetadata();}}@Overridepublic List<String> getServices() {
Applications applications = this.eurekaClient.getApplications();if (applications == null) {
return Collections.emptyList();}List<Application> registered = applications.getRegisteredApplications();List<String> names = new ArrayList<>();for (Application app : registered) {
if (app.getInstances().isEmpty()) {
continue;}names.add(app.getName().toLowerCase());}return names;}}
package com.netflix.discovery;@ImplementedBy(DiscoveryClient.class)
public interface EurekaClient extends LookupService {
Applications getApplicationsForARegion(@Nullable String var1);// 返回当前注册表中所有的服务实例信息Applications getApplications(String var1);// List<InstanceInfo> getInstancesByVipAddress(String var1, boolean var2);List<InstanceInfo> getInstancesByVipAddress(String var1, boolean var2, @Nullable String var3);List<InstanceInfo> getInstancesByVipAddressAndAppName(String var1, String var2, boolean var3);Set<String> getAllKnownRegions();InstanceStatus getInstanceRemoteStatus();/** @deprecated */@DeprecatedList<String> getDiscoveryServiceUrls(String var1);/** @deprecated */@DeprecatedList<String> getServiceUrlsFromConfig(String var1, boolean var2);/** @deprecated */@DeprecatedList<String> getServiceUrlsFromDNS(String var1, boolean var2);/** @deprecated */@Deprecatedvoid registerHealthCheckCallback(HealthCheckCallback var1);// 为Eureka Client注册一个健康检查处理器void registerHealthCheck(HealthCheckHandler var1);// 为Euraka Client 注册一个事件监听器,监听client服务的信息更新void registerEventListener(EurekaEventListener var1);boolean unregisterEventListener(EurekaEventListener var1);HealthCheckHandler getHealthCheckHandler();void shutdown();EurekaClientConfig getEurekaClientConfig();ApplicationInfoManager getApplicationInfoManager();
}
Application持有服务实例信息列表,它可以理解成同一个服务的集群信息,这些服务实例都挂在同一个服务名appName下。InstanceInfo代表一个服务实例信息。Application部分代码如下:
@Serializer("com.netflix.discovery.converters.EntityBodyConverter")
@XStreamAlias("application")
@JsonRootName("application")
public class Application {
private static Random shuffleRandom = new Random();private String name;@XStreamOmitFieldprivate volatile boolean isDirty = false;@XStreamImplicitprivate final Set<InstanceInfo> instances;private final AtomicReference<List<InstanceInfo>> shuffledInstances;private final Map<String, InstanceInfo> instancesMap;public Application() {
instances = new LinkedHashSet<InstanceInfo>();instancesMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, InstanceInfo>();shuffledInstances = new AtomicReference<List<InstanceInfo>>();}public Application(String name) {
this();this.name = StringCache.intern(name);}@JsonCreatorpublic Application(@JsonProperty("name") String name,@JsonProperty("instance") List<InstanceInfo> instances) {
this(name);for (InstanceInfo instanceInfo : instances) {
addInstance(instanceInfo);}}为了保证原子性操作,Application中对InstanceInfo的操作都是同步操作。Applications是注册表中所有服务实例信息的集合,里面的操作大多也是同步操作
Eureka Server一般通过心跳(heartbeats)来识别一个实例的状态。Eureka Client中存在一个定时任务定时通过HealthCheckHandler检测当前Client的状态,如果Client的状态发生改变,将会触发新的注册事件,更新Eureka Server的注册表中该服务实例的相关信息。
EurekaClient来自于com.netflix.discovery包中,其默认实现为com.netflix.discovery. DiscoveryClient,属于eureka-client的源代码,它提供了Eureka Client注册到Server上、续租、下线以及获取Server中注册表信息等诸多关键功能。
- 提供了多种方式获取InstanceInfo,例如根据区域、EurekaServer地址等获取。
- 提供了本地客户端(所处的区域、可用区等)的数据,这部分与AWS密切相关。
- 提供了为客户端注册和获取健康检查处理器的能力
DiscoveryClient 实现了EurekaClient接口,
@Singleton
public class DiscoveryClient implements EurekaClient {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DiscoveryClient.class);// Constantspublic static final String HTTP_X_DISCOVERY_ALLOW_REDIRECT = "X-Discovery-AllowRedirect";private static final String VALUE_DELIMITER = ",";private static final String COMMA_STRING = VALUE_DELIMITER;/*** @deprecated here for legacy support as the client config has moved to be an instance variable*/@Deprecatedprivate static EurekaClientConfig staticClientConfig;// Timersprivate static final String PREFIX = "DiscoveryClient_";private final Counter RECONCILE_HASH_CODES_MISMATCH = Monitors.newCounter(PREFIX + "ReconcileHashCodeMismatch");private final com.netflix.servo.monitor.Timer FETCH_REGISTRY_TIMER = Monitors.newTimer(PREFIX + "FetchRegistry");private final Counter REREGISTER_COUNTER = Monitors.newCounter(PREFIX+ "Reregister");
}
DiscoveryClient 构造函数:
在DiscoveryClient构造函数中,Eureka Client会执行从EurekaServer中拉取注册表信息、服务注册、初始化发送心跳、缓存刷新(重新拉取注册表信息)和按需注册定时任务等操作,可以说DiscoveryClient的构造函数贯穿了Eureka Client启动阶段的各项工作。DiscoveryClient的构造函数传入的参数如下所示
@InjectDiscoveryClient(ApplicationInfoManager applicationInfoManager, EurekaClientConfig config, AbstractDiscoveryClientOptionalArgs args,Provider<BackupRegistry> backupRegistryProvider) {
if (args != null) {
this.healthCheckHandlerProvider = args.healthCheckHandlerProvider;this.healthCheckCallbackProvider = args.healthCheckCallbackProvider;this.eventListeners.addAll(args.getEventListeners());this.preRegistrationHandler = args.preRegistrationHandler;} else {
this.healthCheckCallbackProvider = null;this.healthCheckHandlerProvider = null;this.preRegistrationHandler = null;}this.applicationInfoManager = applicationInfoManager;InstanceInfo myInfo = applicationInfoManager.getInfo();clientConfig = config;staticClientConfig = clientConfig;transportConfig = config.getTransportConfig();instanceInfo = myInfo;if (myInfo != null) {
appPathIdentifier = instanceInfo.getAppName() + "/" + instanceInfo.getId();} else {
logger.warn("Setting instanceInfo to a passed in null value");}this.backupRegistryProvider = backupRegistryProvider;this.urlRandomizer = new EndpointUtils.InstanceInfoBasedUrlRandomizer(instanceInfo);localRegionApps.set(new Applications());fetchRegistryGeneration = new AtomicLong(0);remoteRegionsToFetch = new AtomicReference<String>(clientConfig.fetchRegistryForRemoteRegions());remoteRegionsRef = new AtomicReference<>(remoteRegionsToFetch.get() == null ? null : remoteRegionsToFetch.get().split(","));if (config.shouldFetchRegistry()) {
this.registryStalenessMonitor = new ThresholdLevelsMetric(this, METRIC_REGISTRY_PREFIX + "lastUpdateSec_", new long[]{
15L, 30L, 60L, 120L, 240L, 480L});} else {
this.registryStalenessMonitor = ThresholdLevelsMetric.NO_OP_METRIC;}if (config.shouldRegisterWithEureka()) {
this.heartbeatStalenessMonitor = new ThresholdLevelsMetric(this, METRIC_REGISTRATION_PREFIX + "lastHeartbeatSec_", new long[]{
15L, 30L, 60L, 120L, 240L, 480L});} else {
this.heartbeatStalenessMonitor = ThresholdLevelsMetric.NO_OP_METRIC;}logger.info("Initializing Eureka in region {}", clientConfig.getRegion());if (!config.shouldRegisterWithEureka() && !config.shouldFetchRegistry()) {
logger.info("Client configured to neither register nor query for data.");scheduler = null;heartbeatExecutor = null;cacheRefreshExecutor = null;eurekaTransport = null;instanceRegionChecker = new InstanceRegionChecker(new PropertyBasedAzToRegionMapper(config), clientConfig.getRegion());// This is a bit of hack to allow for existing code using DiscoveryManager.getInstance()// to work with DI'd DiscoveryClientDiscoveryManager.getInstance().setDiscoveryClient(this);DiscoveryManager.getInstance().setEurekaClientConfig(config);initTimestampMs = System.currentTimeMillis();logger.info("Discovery Client initialized at timestamp {} with initial instances count: {}",initTimestampMs, this.getApplications().size());return; // no need to setup up an network tasks and we are done}try {
// default size of 2 - 1 each for heartbeat and cacheRefresh// 定义一个基于线程池的定时器线程池ScheduledExecutorService,线程池大小为2,一个线程用于发送心跳,另一个线程用于缓存刷新,同时定义了发送心跳和缓存刷新线程池scheduler = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(2,new ThreadFactoryBuilder().setNameFormat("DiscoveryClient-%d").setDaemon(true).build());heartbeatExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, clientConfig.getHeartbeatExecutorThreadPoolSize(), 0, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(),new ThreadFactoryBuilder().setNameFormat("DiscoveryClient-HeartbeatExecutor-%d").setDaemon(true).build()); // use direct handoffcacheRefreshExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, clientConfig.getCacheRefreshExecutorThreadPoolSize(), 0, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(),new ThreadFactoryBuilder().setNameFormat("DiscoveryClient-CacheRefreshExecutor-%d").setDaemon(true).build()); // use direct handoff// 初始化Eureka Client与Eureka Server进行HTTP交互的Jersey客户端,将AbstractDiscoveryClientOptionalArgs中的属性用来构建EurekaTransport// EurekaTransport是DiscoveryClient中的一个内部类,其内封装了DiscoveryClient与Eureka Server进行HTTP调用的Jersey客户端eurekaTransport = new EurekaTransport();scheduleServerEndpointTask(eurekaTransport, args);AzToRegionMapper azToRegionMapper;if (clientConfig.shouldUseDnsForFetchingServiceUrls()) {
azToRegionMapper = new DNSBasedAzToRegionMapper(clientConfig);} else {
azToRegionMapper = new PropertyBasedAzToRegionMapper(clientConfig);}if (null != remoteRegionsToFetch.get()) {
azToRegionMapper.setRegionsToFetch(remoteRegionsToFetch.get().split(","));}instanceRegionChecker = new InstanceRegionChecker(azToRegionMapper, clientConfig.getRegion());} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to initialize DiscoveryClient!", e);}// 从Eureka Server中(fetchRegistry方法)拉取注册表信息 下面为true时// 在Eureka Client向EurekaServer注册前,需要先从Eureka Server拉取注册表中的信息,这是服务发现的前提。通过将Eureka Server中的注册表信息缓存到本地,就可以就近获取其他服务的相关信息,减少与Eureka Server的网络通信if (clientConfig.shouldFetchRegistry() && !fetchRegistry(false)) {
fetchRegistryFromBackup();}// 拉取完Eureka Server中的注册表信息后,将对服务实例进行注册// call and execute the pre registration handler before all background tasks (inc registration) is startedif (this.preRegistrationHandler != null) {
this.preRegistrationHandler.beforeRegistration();}if (clientConfig.shouldRegisterWithEureka() && clientConfig.shouldEnforceRegistrationAtInit()) {
try {
// 发起注册服务if (!register() ) {
// 注册失败抛出异常throw new IllegalStateException("Registration error at startup. Invalid server response.");}} catch (Throwable th) {
logger.error("Registration error at startup: {}", th.getMessage());throw new IllegalStateException(th);}}// 初始化任务定时器// finally, init the schedule tasks (e.g. cluster resolvers, heartbeat, instanceInfo replicator, fetchinitScheduledTasks();try {
Monitors.registerObject(this);} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.warn("Cannot register timers", e);}// This is a bit of hack to allow for existing code using DiscoveryManager.getInstance()// to work with DI'd DiscoveryClientDiscoveryManager.getInstance().setDiscoveryClient(this);DiscoveryManager.getInstance().setEurekaClientConfig(config);initTimestampMs = System.currentTimeMillis();logger.info("Discovery Client initialized at timestamp {} with initial instances count: {}",initTimestampMs, this.getApplications().size());}
最后总结一下,在DiscoveryClient的构造函数中,主要依次做了以下的事情:
1)相关配置的赋值,类似ApplicationInfoManager、EurekaClientConfig等。
2)备份注册中心的初始化,默认没有实现。
3)拉取Eureka Server注册表中的信息。
4)注册前的预处理。
5)向Eureka Server注册自身。
6)初始化心跳定时任务、缓存刷新和按需注册等定时任务。
拉取注册表信息
在DiscoveryClient的构造函数中,调用了DiscoveryClient.fetchRegistry方法从Eureka Server中拉取注册表信息
private boolean fetchRegistry(boolean forceFullRegistryFetch) {
Stopwatch tracer = FETCH_REGISTRY_TIMER.start();try {
// If the delta is disabled or if it is the first time, get all// applications// 如果禁用增量,或者applications为null 这是第一次,获取所有Applications applications = getApplications();if (clientConfig.shouldDisableDelta()|| (!Strings.isNullOrEmpty(clientConfig.getRegistryRefreshSingleVipAddress()))|| forceFullRegistryFetch|| (applications == null)|| (applications.getRegisteredApplications().size() == 0)|| (applications.getVersion() == -1)) //Client application does not have latest library supporting delta{
// 省略log信息// 全量拉取注册表信息getAndStoreFullRegistry();} else {
// 增量拉取注册表信息getAndUpdateDelta(applications);}// 计算应用集合一致性哈希码applications.setAppsHashCode(applications.getReconcileHashCode());// 打印注册表上的所有的实例logTotalInstances();} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.error(PREFIX + "{} - was unable to refresh its cache! status = {}", appPathIdentifier, e.getMessage(), e);return false;} finally {
if (tracer != null) {
tracer.stop();}}// Notify about cache refresh before updating the instance remote status// 在更新实例远程状态之前通知有关缓存刷新的信息onCacheRefreshed();// Update remote status based on refreshed data held in the cache // 根据缓存中保存的刷新数据更新远程状态updateInstanceRemoteStatus();// registry was fetched successfully, so return true// 注册表已成功拉取,返回truereturn true;}
一般来讲,在Eureka客户端,除了第一次拉取注册表信息,之后的信息拉取都会尝试只进行增量拉取(第一次拉取注册表信息为全量拉取),下面将分别介绍拉取注册表信息的两种实现getAndStoreFullRegistry() 和 getAndUpdateDelta(applications)
全量拉去注册表信息
一般只有在第一次拉取的时候,才会进行注册表信息的全量拉取,主要在DiscoveryClient.getAndStoreFullRegistry方法中进行
private void getAndStoreFullRegistry() throws Throwable {
// 获取拉取注册表的版本,防止拉取版本落后 long currentUpdateGeneration = fetchRegistryGeneration.get();logger.info("Getting all instance registry info from the eureka server");Applications apps = null;EurekaHttpResponse<Applications> httpResponse = clientConfig.getRegistryRefreshSingleVipAddress() == null? eurekaTransport.queryClient.getApplications(remoteRegionsRef.get()): eurekaTransport.queryClient.getVip(clientConfig.getRegistryRefreshSingleVipAddress(), remoteRegionsRef.get());// 获取成功if (httpResponse.getStatusCode() == Status.OK.getStatusCode()) {
apps = httpResponse.getEntity();}logger.info("The response status is {}", httpResponse.getStatusCode());if (apps == null) {
logger.error("The application is null for some reason. Not storing this information");} else if (fetchRegistryGeneration.compareAndSet(currentUpdateGeneration, currentUpdateGeneration + 1)) {
// 从apps中筛选出状态为UP的实例,同时打乱实例的顺序,防止同一服务的不同实例在启动时接受流量localRegionApps.set(this.filterAndShuffle(apps));logger.debug("Got full registry with apps hashcode {}", apps.getAppsHashCode());} else {
logger.warn("Not updating applications as another thread is updating it already");}}
全量拉取将从Eureka Server中拉取注册表中所有的服务实例信息(封装在Applications中),并经过处理后替换掉本地注册表缓存Applications
getAndStoreFullRegistry方法可能被多个线程同时调用,导致新拉取的注册表被旧的注册表覆盖(有可能出现先拉取注册表信息的线程在覆盖apps时被阻塞,被后拉取注册表信息的线程抢先设置了apps,被阻塞的线程恢复后再次设置了apps,导致apps数据版本落后),产生脏数据,对此,Eureka通过类型为AtomicLong的currentUpdateGeneration对apps的更新版本进行跟踪。如果更新版本不一致,说明本次拉取注册表信息已过时,不需要缓存到本地。拉取到注册表信息之后会对获取到的apps进行筛选,只保留状态为UP的服务实例信息
增量拉取注册表信息
增量式的拉取方式,一般发生在第一次拉取注册表信息之后,拉取的信息定义为从某一段时间之后发生的所有变更信息,通常来讲是3分钟之内注册表的信息变化。在获取到更新的delta后,会根据delta中的增量更新对本地的数据进行更新。与getAndStoreFullRegistry方法一样,也通过fetchRegistryGeneration对更新的版本进行控制。增量式拉取是为了维护Eureka Client本地的注册表信息与Eureka Server注册表信息的一致性,防止数据过久而失效,采用增量式拉取的方式减少了拉取注册表信息的通信量。Client中有一个注册表缓存刷新定时器专门负责维护两者之间信息的同步性。但是当增量式拉取出现意外时,定时器将执行全量拉取以更新本地缓存的注册表信息。具体代码如下所示。
private void getAndUpdateDelta(Applications applications) throws Throwable {
long currentUpdateGeneration = fetchRegistryGeneration.get();Applications delta = null;EurekaHttpResponse<Applications> httpResponse = eurekaTransport.queryClient.getDelta(remoteRegionsRef.get());if (httpResponse.getStatusCode() == Status.OK.getStatusCode()) {
delta = httpResponse.getEntity();}// 获取增量拉取失败if (delta == null) {
logger.warn("The server does not allow the delta revision to be applied because it is not safe. "+ "Hence got the full registry.");// 进行全量拉取getAndStoreFullRegistry();} else if (fetchRegistryGeneration.compareAndSet(currentUpdateGeneration, currentUpdateGeneration + 1)) {
logger.debug("Got delta update with apps hashcode {}", delta.getAppsHashCode());String reconcileHashCode = "";if (fetchRegistryUpdateLock.tryLock()) {
try {
// 更新本地缓存updateDelta(delta);// 计算应用集合一致性哈希表reconcileHashCode = getReconcileHashCode(applications);} finally {
fetchRegistryUpdateLock.unlock();}} else {
logger.warn("Cannot acquire update lock, aborting getAndUpdateDelta");}// There is a diff in number of instances for some reason// 比较应用集合一致性哈希吗,如果不一致将认为本次增量式拉取数据胰脏,将发起全量拉取更新本地注册表信息if (!reconcileHashCode.equals(delta.getAppsHashCode()) || clientConfig.shouldLogDeltaDiff()) {
reconcileAndLogDifference(delta, reconcileHashCode); // this makes a remoteCall}} else {
logger.warn("Not updating application delta as another thread is updating it already");logger.debug("Ignoring delta update with apps hashcode {}, as another thread is updating it already", delta.getAppsHashCode());}}
更新本地缓存updateDelta(delta);
private void updateDelta(Applications delta) {
int deltaCount = 0;for (Application app : delta.getRegisteredApplications()) {
for (InstanceInfo instance : app.getInstances()) {
Applications applications = getApplications();String instanceRegion = instanceRegionChecker.getInstanceRegion(instance);if (!instanceRegionChecker.isLocalRegion(instanceRegion)) {
Applications remoteApps = remoteRegionVsApps.get(instanceRegion);if (null == remoteApps) {
remoteApps = new Applications();remoteRegionVsApps.put(instanceRegion, remoteApps);}applications = remoteApps;}++deltaCount;// 变更类型为ADDEDif (ActionType.ADDED.equals(instance.getActionType())) {
Application existingApp = applications.getRegisteredApplications(instance.getAppName());if (existingApp == null) {
applications.addApplication(app);}logger.debug("Added instance {} to the existing apps in region {}", instance.getId(), instanceRegion);// 添加到本地注册表中applications.getRegisteredApplications(instance.getAppName()).addInstance(instance);} else if (ActionType.MODIFIED.equals(instance.getActionType())) {
// 变更类型为 MODIFIEDApplication existingApp = applications.getRegisteredApplications(instance.getAppName());if (existingApp == null) {
applications.addApplication(app);}logger.debug("Modified instance {} to the existing apps ", instance.getId());// 添加到本地注册表中applications.getRegisteredApplications(instance.getAppName()).addInstance(instance);} else if (ActionType.DELETED.equals(instance.getActionType())) {
// 变更类型为 DELETEDApplication existingApp = applications.getRegisteredApplications(instance.getAppName());if (existingApp == null) {
applications.addApplication(app);}logger.debug("Deleted instance {} to the existing apps ", instance.getId());// 从注册表中删除applications.getRegisteredApplications(instance.getAppName()).removeInstance(instance);}}}logger.debug("The total number of instances fetched by the delta processor : {}", deltaCount);getApplications().setVersion(delta.getVersion());getApplications().shuffleInstances(clientConfig.shouldFilterOnlyUpInstances());for (Applications applications : remoteRegionVsApps.values()) {
applications.setVersion(delta.getVersion());applications.shuffleInstances(clientConfig.shouldFilterOnlyUpInstances());}}
更新本地注册表缓存之后,Eureka Client会通过getReconcileHashCode计算合并后的Applications的appsHashCode(应用集合一致性哈希码),和Eureka Server传递的delta上的appsHashCode进行比较(delta中携带的appsHashCode通过Eureka Server的全量注册表计算得出),比对客户端和服务端上注册表的差异。如果哈希值不一致的话将再调用一次getAndStoreFullRegistry获取全量数据保证EurekaClient与Eureka Server之间注册表数据的一致
计算hash一致性 getReconcileHashCode()
private String getReconcileHashCode(Applications applications) {
TreeMap<String, AtomicInteger> instanceCountMap = new TreeMap<String, AtomicInteger>();if (isFetchingRemoteRegionRegistries()) {
for (Applications remoteApp : remoteRegionVsApps.values()) {
remoteApp.populateInstanceCountMap(instanceCountMap);}}applications.populateInstanceCountMap(instanceCountMap);return Applications.getReconcileHashCode(instanceCountMap);}
服务注册
在拉取完Eureka Server中的注册表信息并将其缓存在本地后,Eureka Client将向Eureka Server注册自身服务实例元数据,主要逻辑位于DiscoveryClent.register()方法中。register方法代码如下所示:
// 通过进行适当的REST调用来注册eureka服务
boolean register() throws Throwable {
logger.info(PREFIX + "{}: registering service...", appPathIdentifier);EurekaHttpResponse<Void> httpResponse;try {
httpResponse = eurekaTransport.registrationClient.register(instanceInfo);} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn(PREFIX + "{} - registration failed {}", appPathIdentifier, e.getMessage(), e);throw e;}if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info(PREFIX + "{} - registration status: {}", appPathIdentifier, httpResponse.getStatusCode());}return httpResponse.getStatusCode() == 204;}
Eureka Client会将自身服务实例元数据(封装在InstanceInfo中)发送到Eureka Server中请求服务注册,当Eureka Server返回204状态码时,说明服务注册成功.
初始化定时任务
很明显,服务注册应该是一个持续的过程,Eureka Client通过定时发送心跳的方式与Eureka Server进行通信,维持自己在Server注册表上的租约。同时Eureka Server注册表中的服务实例信息是动态变化的,为了保持Eureka Client与Eureka Server的注册表信息的一致性,Eureka Client需要定时向EurekaServer拉取注册表信息并更新本地缓存。为了监控EurekaClient应用信息和状态的变化,Eureka Client设置了一个按需注册定时器,定时检查应用信息或者状态的变化,并在发生变化时向Eureka Server重新注册,避免注册表中的本服务实例信息不可用。在DiscoveryClient.initScheduledTasks方法中初始化了三个定时器任务,一个用于向Eureka Server拉取注册表信息刷新本地缓存;一个用于向Eureka Server发送心跳;一个用于进行按需注册的操作。
private void initScheduledTasks() {
if (clientConfig.shouldFetchRegistry()) {
// registry cache refresh timer// 注册表缓存刷新定时器,获取配置文件中刷新间隔,默认为30秒,可通过eureka.client.registry-fetch-interval-seconds 进行设置int registryFetchIntervalSeconds = clientConfig.getRegistryFetchIntervalSeconds();int expBackOffBound = clientConfig.getCacheRefreshExecutorExponentialBackOffBound();scheduler.schedule(new TimedSupervisorTask("cacheRefresh",scheduler,cacheRefreshExecutor,registryFetchIntervalSeconds,TimeUnit.SECONDS,expBackOffBound,new CacheRefreshThread()),registryFetchIntervalSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS);}if (clientConfig.shouldRegisterWithEureka()) {
// 发送心跳定时器,默认30秒发送一次。// 发送心跳定时器,默认30秒发送一次。/*** 通过InstanceInfo类中的获取LeaseInfo类* private volatile LeaseInfo leaseInfo;** @JsonRootName("leaseInfo")public class LeaseInfo {public static final int DEFAULT_LEASE_RENEWAL_INTERVAL = 30;public static final int DEFAULT_LEASE_DURATION = 90;// Client settingsprivate int renewalIntervalInSecs = DEFAULT_LEASE_RENEWAL_INTERVAL;private int durationInSecs = DEFAULT_LEASE_DURATION;}*/int renewalIntervalInSecs = instanceInfo.getLeaseInfo().getRenewalIntervalInSecs();int expBackOffBound = clientConfig.getHeartbeatExecutorExponentialBackOffBound();logger.info("Starting heartbeat executor: " + "renew interval is: {}", renewalIntervalInSecs);// 心跳定时器// Heartbeat timerscheduler.schedule(new TimedSupervisorTask("heartbeat",scheduler,heartbeatExecutor,renewalIntervalInSecs,TimeUnit.SECONDS,expBackOffBound,new HeartbeatThread()),renewalIntervalInSecs, TimeUnit.SECONDS);// 按需注册定时器// InstanceInfo replicatorinstanceInfoReplicator = new InstanceInfoReplicator(this,instanceInfo,clientConfig.getInstanceInfoReplicationIntervalSeconds(),2); // burstSize// 监控应用的status变化,发生变化即可发起重新注册 statusChangeListener = new ApplicationInfoManager.StatusChangeListener() {
@Overridepublic String getId() {
return "statusChangeListener";}@Overridepublic void notify(StatusChangeEvent statusChangeEvent) {
if (InstanceStatus.DOWN == statusChangeEvent.getStatus() ||InstanceStatus.DOWN == statusChangeEvent.getPreviousStatus()) {
// log at warn level if DOWN was involvedlogger.warn("Saw local status change event {}", statusChangeEvent);} else {
logger.info("Saw local status change event {}", statusChangeEvent);}instanceInfoReplicator.onDemandUpdate();}};if (clientConfig.shouldOnDemandUpdateStatusChange()) {
//注册应用状态改变监控器applicationInfoManager.registerStatusChangeListener(statusChangeListener);}// 启动定时按需注册定时任务instanceInfoReplicator.start(clientConfig.getInitialInstanceInfoReplicationIntervalSeconds());} else {
logger.info("Not registering with Eureka server per configuration");}}
缓存刷新定时任务与发送心跳定时任务
在DiscoveryClient .initScheduledTasks()方法中,通过ScheduledExecutorService.schedule()的方式提交缓存刷新任务和发送心跳任务,任务执行的方式为延时执行并且不循环,这两个任务的定时循环逻辑由TimedSupervisorTask提供实现。TimedSupervisorTask继承了TimerTask,提供执行定时任务的功能。它在run方法中定义执行定时任务的逻辑。具体代码如下所示
public class TimedSupervisorTask extends TimerTask {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(TimedSupervisorTask.class);private final Counter timeoutCounter;private final Counter rejectedCounter;private final Counter throwableCounter;private final LongGauge threadPoolLevelGauge;private final ScheduledExecutorService scheduler;private final ThreadPoolExecutor executor;private final long timeoutMillis;private final Runnable task;private final AtomicLong delay;private final long maxDelay;public TimedSupervisorTask(String name, ScheduledExecutorService scheduler, ThreadPoolExecutor executor,int timeout, TimeUnit timeUnit, int expBackOffBound, Runnable task) {
this.scheduler = scheduler;this.executor = executor;this.timeoutMillis = timeUnit.toMillis(timeout);this.task = task;this.delay = new AtomicLong(timeoutMillis);this.maxDelay = timeoutMillis * expBackOffBound;// Initialize the counters and register.timeoutCounter = Monitors.newCounter("timeouts");rejectedCounter = Monitors.newCounter("rejectedExecutions");throwableCounter = Monitors.newCounter("throwables");threadPoolLevelGauge = new LongGauge(MonitorConfig.builder("threadPoolUsed").build());Monitors.registerObject(name, this);}@Overridepublic void run() {
Future<?> future = null;try {
// 执行任务future = executor.submit(task);threadPoolLevelGauge.set((long) executor.getActiveCount());// 等待任务执行结果future.get(timeoutMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); // block until done or timeout// 执行完成设置下次时间间隔delay.set(timeoutMillis);threadPoolLevelGauge.set((long) executor.getActiveCount());} catch (TimeoutException e) {
logger.warn("task supervisor timed out", e);// 任务超时timeoutCounter.increment();long currentDelay = delay.get();long newDelay = Math.min(maxDelay, currentDelay * 2);delay.compareAndSet(currentDelay, newDelay);} catch (RejectedExecutionException e) {
if (executor.isShutdown() || scheduler.isShutdown()) {
logger.warn("task supervisor shutting down, reject the task", e);} else {
logger.warn("task supervisor rejected the task", e);}// 执行任务被拒绝,统计拒绝次数rejectedCounter.increment();} catch (Throwable e) {
if (executor.isShutdown() || scheduler.isShutdown()) {
logger.warn("task supervisor shutting down, can't accept the task");} else {
logger.warn("task supervisor threw an exception", e);}throwableCounter.increment();} finally {
// 取消未结束的任务if (future != null) {
future.cancel(true);}// 如果定时任务服务未关闭,定义下一次任务if (!scheduler.isShutdown()) {
scheduler.schedule(this, delay.get(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);}}}
}
run方法中存在以下的任务调度过程:
1)scheduler初始化并延迟执行TimedSupervisorTask;
2)TimedSupervisorTask将task提交executor中执行,task和executor在初始化TimedSupervisorTask时传入:
□ 若task正常执行,TimedSupervisorTask将自己提交到scheduler,延迟delay时间后再次执行;
□ 若task执行超时,计算新的delay时间(不超过maxDelay),TimedSupervisorTask将自己提交到scheduler,延迟delay时间后再次执行;

TimedSupervisorTask通过这种不断循环提交任务的方式,完成定时执行任务的要求
按需注册定时任务
按需注册定时任务的作用是当Eureka Client中的InstanceInfo或者status发生变化时,重新向Eureka Server发起注册请求,更新注册表中的服务实例信息,保证Eureka Server注册表中服务实例信息有效和可用。initScheduledTasks()中分离出的部分代码
// 按需注册定时器// InstanceInfo replicatorinstanceInfoReplicator = new InstanceInfoReplicator(this,instanceInfo,clientConfig.getInstanceInfoReplicationIntervalSeconds(),2); // burstSize// 监控应用的status变化,发生变化即可发起重新注册 statusChangeListener = new ApplicationInfoManager.StatusChangeListener() {
@Overridepublic String getId() {
return "statusChangeListener";}@Overridepublic void notify(StatusChangeEvent statusChangeEvent) {
if (InstanceStatus.DOWN == statusChangeEvent.getStatus() ||InstanceStatus.DOWN == statusChangeEvent.getPreviousStatus()) {
// log at warn level if DOWN was involvedlogger.warn("Saw local status change event {}", statusChangeEvent);} else {
logger.info("Saw local status change event {}", statusChangeEvent);}instanceInfoReplicator.onDemandUpdate();}};if (clientConfig.shouldOnDemandUpdateStatusChange()) {
//注册应用状态改变监控器applicationInfoManager.registerStatusChangeListener(statusChangeListener);}// 启动定时按需注册定时任务instanceInfoReplicator.start(clientConfig.getInitialInstanceInfoReplicationIntervalSeconds());} else {
logger.info("Not registering with Eureka server per configuration");}
按需注册分为两部分,一部分是定义了一个定时任务,定时刷新服务实例的信息和检查应用状态的变化,在服务实例信息发生改变的情况下向Eureka Server重新发起注册操作;另一部分是注册了状态改变监控器,在应用状态发生变化时,刷新服务实例信息,在服务实例信息发生改变的情况下向Eureka Server重新发起注册操作
/** *用于将本地instanceinfo更新和复制到远程服务器的任务。 此任务的属性是:-配置有单个更新线程以确保对远程服务器进行顺序更新-可以通过onDemandUpdate()按需计划更新任务-任务处理的速率受burstSize限制-始终计划新的更新任务自动执行较早的更新任务后。 但是,如果启动了按需任务,则计划的自动更新任务将被丢弃(并且在新的按需更新之后将安排新的任务) */
class InstanceInfoReplicator implements Runnable {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(InstanceInfoReplicator.class);private final DiscoveryClient discoveryClient;private final InstanceInfo instanceInfo;private final int replicationIntervalSeconds;private final ScheduledExecutorService scheduler;private final AtomicReference<Future> scheduledPeriodicRef;private final AtomicBoolean started;private final RateLimiter rateLimiter;private final int burstSize;private final int allowedRatePerMinute;InstanceInfoReplicator(DiscoveryClient discoveryClient, InstanceInfo instanceInfo, int replicationIntervalSeconds, int burstSize) {
this.discoveryClient = discoveryClient;this.instanceInfo = instanceInfo;this.scheduler = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1,new ThreadFactoryBuilder().setNameFormat("DiscoveryClient-InstanceInfoReplicator-%d").setDaemon(true).build());this.scheduledPeriodicRef = new AtomicReference<Future>();this.started = new AtomicBoolean(false);this.rateLimiter = new RateLimiter(TimeUnit.MINUTES);this.replicationIntervalSeconds = replicationIntervalSeconds;this.burstSize = burstSize;this.allowedRatePerMinute = 60 * this.burstSize / this.replicationIntervalSeconds;logger.info("InstanceInfoReplicator onDemand update allowed rate per min is {}", allowedRatePerMinute);}public void start(int initialDelayMs) {
if (started.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
instanceInfo.setIsDirty(); // for initial registerFuture next = scheduler.schedule(this, initialDelayMs, TimeUnit.SECONDS);scheduledPeriodicRef.set(next);}}public void stop() {
shutdownAndAwaitTermination(scheduler);started.set(false);}private void shutdownAndAwaitTermination(ExecutorService pool) {
pool.shutdown();try {
if (!pool.awaitTermination(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
pool.shutdownNow();}} catch (InterruptedException e) {
logger.warn("InstanceInfoReplicator stop interrupted");}}public boolean onDemandUpdate() {
if (rateLimiter.acquire(burstSize, allowedRatePerMinute)) {
if (!scheduler.isShutdown()) {
scheduler.submit(new Runnable() {
@Overridepublic void run() {
logger.debug("Executing on-demand update of local InstanceInfo");Future latestPeriodic = scheduledPeriodicRef.get();if (latestPeriodic != null && !latestPeriodic.isDone()) {
logger.debug("Canceling the latest scheduled update, it will be rescheduled at the end of on demand update");latestPeriodic.cancel(false);}InstanceInfoReplicator.this.run();}});return true;} else {
logger.warn("Ignoring onDemand update due to stopped scheduler");return false;}} else {
logger.warn("Ignoring onDemand update due to rate limiter");return false;}}public void run() {
try {
// 刷新了InstanceInfo中的服务实例信息discoveryClient.refreshInstanceInfo();// 如果数据发生改变,则返回数据更新时间Long dirtyTimestamp = instanceInfo.isDirtyWithTime();if (dirtyTimestamp != null) {
// 注册服务实例discoveryClient.register();// 重置更新状态instanceInfo.unsetIsDirty(dirtyTimestamp);}} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn("There was a problem with the instance info replicator", t);} finally {
// 执行下一个延时任务Future next = scheduler.schedule(this, replicationIntervalSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS);scheduledPeriodicRef.set(next);}}}DiscoveryClient中刷新本地服务实例信息和检查服务状态变化的代码如下refreshInstanceInfo()方法:
void refreshInstanceInfo() {
// 刷新服务实例信息applicationInfoManager.refreshDataCenterInfoIfRequired();// 更新租约信息 applicationInfoManager.refreshLeaseInfoIfRequired();InstanceStatus status;try {
// 检查服务实例的变化status = getHealthCheckHandler().getStatus(instanceInfo.getStatus());} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn("Exception from healthcheckHandler.getStatus, setting status to DOWN", e);status = InstanceStatus.DOWN;}if (null != status) {
applicationInfoManager.setInstanceStatus(status);}}
run方法首先调用了discoveryClient#refreshInstanceInfo方法刷新当前的服务实例信息,查看当前服务实例信息和服务状态是否发生变化,如果当前服务实例信息或者服务状态发生变化将向Eureka Server重新发起服务注册操作。最后声明了下一个延时任务,用于再次调用run方法,继续检查服务实例信息和服务状态的变化,在服务实例信息发生变化的情况下重新发起注册。如果Eureka Client的状态发生变化(在Spring Boot通过Actuator对服务状态进行监控,具体实现为EurekaHealthCheckHandler),注册在ApplicationInfoManager的状态改变监控器将会被触发,从而调用InstanceInfoReplicator#onDemandUpdate方法,检查服务实例信息和服务状态的变化,可能会引发按需注册任务。代码如下所示
// InstanceInfoReplicator#onDemandUpdate方法
public boolean onDemandUpdate() {
// 控制流量,当超过限制时,不能进行按需更新if (rateLimiter.acquire(burstSize, allowedRatePerMinute)) {
if (!scheduler.isShutdown()) {
scheduler.submit(new Runnable() {
@Overridepublic void run() {
logger.debug("Executing on-demand update of local InstanceInfo");Future latestPeriodic = scheduledPeriodicRef.get();// 取消上次run任务if (latestPeriodic != null && !latestPeriodic.isDone()) {
logger.debug("Canceling the latest scheduled update, it will be rescheduled at the end of on demand update");latestPeriodic.cancel(false);}InstanceInfoReplicator.this.run();}});return true;} else {
logger.warn("Ignoring onDemand update due to stopped scheduler");return false;}} else {
logger.warn("Ignoring onDemand update due to rate limiter");return false;}}
InstanceInfoReplicator#onDemandUpdate方法调用InstanceInfoReplicator#run方法检查服务实例信息和服务状态的变化,并在服务实例信息发生变化的情况下向Eureka Server发起重新注册的请求。为了防止重复执行run方法,onDemandUpdate方法还会取消执行上次已提交且未完成的run方法,执行最新的按需注册任务

服务下线
一般情况下,应用服务在关闭的时候,Eureka Client会主动向Eureka Server注销自身在注册表中的信息。DiscoveryClient中对象销毁前执行的清理方法
@PreDestroy@Overridepublic synchronized void shutdown() {
if (isShutdown.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
logger.info("Shutting down DiscoveryClient ...");// 原子操作,确保只会执行一次if (statusChangeListener != null && applicationInfoManager != null) {
// 注销状态监听器applicationInfoManager.unregisterStatusChangeListener(statusChangeListener.getId());}
// 取消定时任务cancelScheduledTasks();// If APPINFO was registeredif (applicationInfoManager != null&& clientConfig.shouldRegisterWithEureka()&& clientConfig.shouldUnregisterOnShutdown()) {
// 服务下线applicationInfoManager.setInstanceStatus(InstanceStatus.DOWN);unregister();}
// 关闭Jesry客户端if (eurekaTransport != null) {
eurekaTransport.shutdown();}// 关闭相关的监视器heartbeatStalenessMonitor.shutdown();registryStalenessMonitor.shutdown();logger.info("Completed shut down of DiscoveryClient");}}
Eureka Server源码解析
Eureka Server作为一个开箱即用的服务注册中心,提供了以下的功能,用以满足与Eureka Client交互的需求:
- 服务注册
- 接受服务心跳
- 服务剔除
- 服务下线
- 集群同步
- 获取注册表中服务实例信息
需要注意的是,Eureka Server同时也是一个Eureka Client,在不禁止EurekaServer的客户端行为时,它会向它配置文件中的其他Eureka Server进行拉取注册表、服务注册和发送心跳等操作
服务实例注册表
InstanceRegistry是Eureka Server中注册表管理的核心接口。它的类结构如下图所示。图中出现了两个InstanceRegistry,最下面的InstanceRegistry对EurekaServer的注册表实现类PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl进行了继承和扩展,使其适配Spring Cloud的使用环境,主要实现由PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl提供
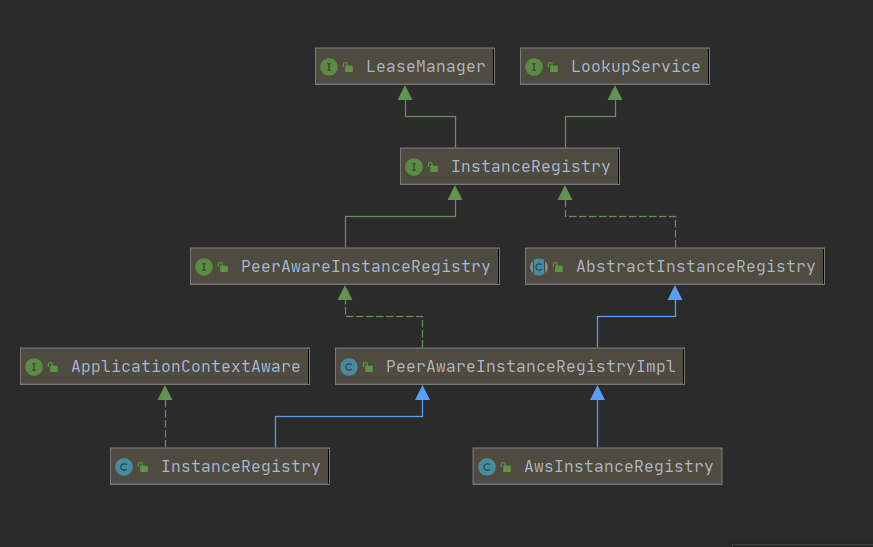
上层的InstanceRegistry是Eureka Server注册表的最核心接口,其职责是在内存中管理注册到Eureka Server中的服务实例信息。InstanceRegistry分别继承了LeaseManager和LookupService接口。LeaseManager接口的功能是对注册到Eureka Server中的服务实例租约进行管理。而LookupService提供对服务实例进行检索的功能,在Eureka Client的源码解析中已进行介绍,在此不对其接口进行展示。LeaseManager接口提供的方法代码如下所示
public interface LeaseManager<T> {
void register(T r, int leaseDuration, boolean isReplication);boolean cancel(String appName, String id, boolean isReplication);boolean renew(String appName, String id, boolean isReplication);void evict();
}
LeaseManager接口作用是对注册到Eureka Server中的服务实例租约进行管理,分别有服务注册、服务下线、服务租约更新以及服务剔除等操作。
LeaseManager中管理的对象是Lease, Lease代表一个Eureka Client服务实例信息的租约,它提供了对其内持有的类的时间有效性操作。Lease持有的类是代表服务实例信息的InstanceInfo。Lease中定义了租约的操作类型,分别是注册、下线、更新,同时提供了对租约中时间属性的各项操作。租约默认有效时长(duration)为90秒。InstanceRegistry在继承LeaseManager和LookupService接口的基础上,还添加了一些特有的方法,可以更为简单地管理服务实例租约和查询注册表中的服务实例信息。可以通过AbstractInstanceRegistry查看InstanceRegistry接口方法的具体实现。PeerAwareInstanceRegistry继承了InstanceRegistry接口,在其基础上添加了Eureka Server集群同步的操作,其实现类PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl继承了AbstractInstanceRegistry的实现,在对本地注册表操作的基础上添加了对其peer节点的同步复制操作,使得Eureka Server集群中的注册表信息保持一致
服务注册
Eureka Client在发起服务注册时会将自身的服务实例元数据封装在InstanceInfo中,然后将InstanceInfo发送到Eureka Server。Eureka Server在接收到Eureka Client发送的InstanceInfo后将会尝试将其放到本地注册表中以供其他Eureka Client进行服务发现。服务注册的主要实现位于AbstractInstanceRegistry的registry方法中。
在register中,服务实例的InstanceInfo保存在Lease中,Lease在AbstractInstanceRegistry中统一通过ConcurrentHashMap保存在内存中。在服务注册过程中,会先获取一个读锁,防止其他线程对registry注册表进行数据操作,避免数据的不一致。然后从resgitry查询对应的InstanceInfo租约是否已经存在注册表中,根据appName划分服务集群,使用InstanceId唯一标记服务实例。如果租约存在,比较两个租约中的InstanceInfo的最后更新时间lastDirtyTimestamp,保留时间戳大的服务实例信息InstanceInfo。如果租约不存在,意味这是一次全新的服务注册,将会进行自我保护的统计,创建新的租约保存InstanceInfo。接着将租约放到resgitry注册表中。之后将进行一系列缓存操作并根据覆盖状态规则设置服务实例的状态,缓存操作包括将InstanceInfo加入用于统计EurekaClient增量式获取注册表信息的recentlyChangedQueue和失效responseCache中对应的缓存。最后设置服务实例租约的上线时间用于计算租约的有效时间,释放读锁并完成服务注册。
/*** Registers a new instance with a given duration.** @see com.netflix.eureka.lease.LeaseManager#register(java.lang.Object, int, boolean)*/public void register(InstanceInfo registrant, int leaseDuration, boolean isReplication) {
try {
// 获取锁read.lock();// 这里的registry是ConConcurrentHashMap 根据appName对服务集群进行分类Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> gMap = registry.get(registrant.getAppName());REGISTER.increment(isReplication);if (gMap == null) {
final ConcurrentHashMap<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> gNewMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>>();// 这里有一个比较严谨的操作,防止在添加新的服务实例集群租约时,把已有的其他线程的集群租约覆盖掉,如果存在该键值,直接返回值,否则添加该键值对,返回null gMap = registry.putIfAbsent(registrant.getAppName(), gNewMap);if (gMap == null) {
gMap = gNewMap;}}// 根据instanceId获取实例的租约Lease<InstanceInfo> existingLease = gMap.get(registrant.getId());// Retain the last dirty timestamp without overwriting it, if there is already a leaseif (existingLease != null && (existingLease.getHolder() != null)) {
Long existingLastDirtyTimestamp = existingLease.getHolder().getLastDirtyTimestamp();Long registrationLastDirtyTimestamp = registrant.getLastDirtyTimestamp();logger.debug("Existing lease found (existing={}, provided={}", existingLastDirtyTimestamp, registrationLastDirtyTimestamp);// this is a > instead of a >= because if the timestamps are equal, we still take the remote transmitted// InstanceInfo instead of the server local copy.// 如果该实例的租约已经存在,比较最后更新时间戳的大小,取最大值的注册信息为有效if (existingLastDirtyTimestamp > registrationLastDirtyTimestamp) {
logger.warn("There is an existing lease and the existing lease's dirty timestamp {} is greater" +" than the one that is being registered {}", existingLastDirtyTimestamp, registrationLastDirtyTimestamp);logger.warn("Using the existing instanceInfo instead of the new instanceInfo as the registrant");registrant = existingLease.getHolder();}} else {
// The lease does not exist and hence it is a new registration// 如果租约不存在,这时一个新的注册实例synchronized (lock) {
if (this.expectedNumberOfRenewsPerMin > 0) {
// Since the client wants to cancel it, reduce the threshold// 自我保护机制// (1// for 30 seconds, 2 for a minute)this.expectedNumberOfRenewsPerMin = this.expectedNumberOfRenewsPerMin + 2;this.numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold =(int) (this.expectedNumberOfRenewsPerMin * serverConfig.getRenewalPercentThreshold());}}logger.debug("No previous lease information found; it is new registration");}// 创建新租约Lease<InstanceInfo> lease = new Lease<InstanceInfo>(registrant, leaseDuration);if (existingLease != null) {
// 如果租约存在,继承租约的服务上线初始时间lease.setServiceUpTimestamp(existingLease.getServiceUpTimestamp());}// 保存租约gMap.put(registrant.getId(), lease);// 添加最近注册的对列,用来统计最近注册服务实例的数据synchronized (recentRegisteredQueue) {
recentRegisteredQueue.add(new Pair<Long, String>(System.currentTimeMillis(),registrant.getAppName() + "(" + registrant.getId() + ")"));}// This is where the initial state transfer of overridden status happensif (!InstanceStatus.UNKNOWN.equals(registrant.getOverriddenStatus())) {
logger.debug("Found overridden status {} for instance {}. Checking to see if needs to be add to the "+ "overrides", registrant.getOverriddenStatus(), registrant.getId());if (!overriddenInstanceStatusMap.containsKey(registrant.getId())) {
logger.info("Not found overridden id {} and hence adding it", registrant.getId());overriddenInstanceStatusMap.put(registrant.getId(), registrant.getOverriddenStatus());}}// 根据覆盖状态规则得到服务实例的最终状态,并设置服务实例的当前状态InstanceStatus overriddenStatusFromMap = overriddenInstanceStatusMap.get(registrant.getId());if (overriddenStatusFromMap != null) {
logger.info("Storing overridden status {} from map", overriddenStatusFromMap);registrant.setOverriddenStatus(overriddenStatusFromMap);}// Set the status based on the overridden status rulesInstanceStatus overriddenInstanceStatus = getOverriddenInstanceStatus(registrant, existingLease, isReplication);registrant.setStatusWithoutDirty(overriddenInstanceStatus);// If the lease is registered with UP status, set lease service up timestamp// 如果服务实例状态为up设置租约的服务上线时间,只有第一次设置有效if (InstanceStatus.UP.equals(registrant.getStatus())) {
lease.serviceUp();}registrant.setActionType(ActionType.ADDED);// 添加最近租约变更记录队列,标识ActionType为ADDED// 这将用于Eureka Client 增量式获取注册表信息// recentlyChangedQueue.add(new RecentlyChangedItem(lease));// 设置服务实例信息更新时间registrant.setLastUpdatedTimestamp();// 设置response缓存过期,这将用于Eureka Client全量获取注册表信息invalidateCache(registrant.getAppName(), registrant.getVIPAddress(), registrant.getSecureVipAddress());logger.info("Registered instance {}/{} with status {} (replication={})",registrant.getAppName(), registrant.getId(), registrant.getStatus(), isReplication);} finally {
// 释放锁read.unlock();}}
接受服务心跳
在Eureka Client完成服务注册之后,它需要定时向EurekaServer发送心跳请求(默认30秒一次),维持自己在EurekaServer中租约的有效性。Eureka Server处理心跳请求的核心逻辑位于AbstractInstanceRegistry#renew方法中。renew方法是对Eureka Client位于注册表中的租约的续租操作,不像register方法需要服务实例信息,仅根据服务实例的服务名和服务实例id即可更新对应租约的有效时间
public boolean renew(String appName, String id, boolean isReplication) {
RENEW.increment(isReplication);// 根据appName获取集群的租约集合Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> gMap = registry.get(appName);Lease<InstanceInfo> leaseToRenew = null;if (gMap != null) {
leaseToRenew = gMap.get(id);}// 租约不存在,直接返回falseif (leaseToRenew == null) {
RENEW_NOT_FOUND.increment(isReplication);logger.warn("DS: Registry: lease doesn't exist, registering resource: {} - {}", appName, id);return false;} else {
// 根据覆盖状态规则得到服务实例的最终状态InstanceInfo instanceInfo = leaseToRenew.getHolder();if (instanceInfo != null) {
// touchASGCache(instanceInfo.getASGName());InstanceStatus overriddenInstanceStatus = this.getOverriddenInstanceStatus(instanceInfo, leaseToRenew, isReplication);if (overriddenInstanceStatus == InstanceStatus.UNKNOWN) {
logger.info("Instance status UNKNOWN possibly due to deleted override for instance {}"+ "; re-register required", instanceInfo.getId());// 如果得到的服务实例最后状态是UNKNOWN,取消续约RENEW_NOT_FOUND.increment(isReplication);return false;}if (!instanceInfo.getStatus().equals(overriddenInstanceStatus)) {
logger.info("The instance status {} is different from overridden instance status {} for instance {}. "+ "Hence setting the status to overridden status", instanceInfo.getStatus().name(),instanceInfo.getOverriddenStatus().name(),instanceInfo.getId());instanceInfo.setStatusWithoutDirty(overriddenInstanceStatus);}}// 统计每分钟租约续租的次数,用于自我保护renewsLastMin.increment();// 更新租约的有效时间leaseToRenew.renew();return true;}}/*** @return The rule that will process the instance status override.*/protected abstract InstanceStatusOverrideRule getInstanceInfoOverrideRule();protected InstanceInfo.InstanceStatus getOverriddenInstanceStatus(InstanceInfo r,Lease<InstanceInfo> existingLease,boolean isReplication) {
InstanceStatusOverrideRule rule = getInstanceInfoOverrideRule();logger.debug("Processing override status using rule: {}", rule);return rule.apply(r, existingLease, isReplication).status();}
在#renew方法中,不关注InstanceInfo,仅关注于租约本身以及租约的服务实例状态。如果根据服务实例的appName和instanceInfoId查询出服务实例的租约,并且根据#getOverriddenInstanceStatus方法得到的instanceStatus不为InstanceStatus.UNKNOWN,那么更新租约中的有效时间,即更新租约Lease中的lastUpdateTimestamp,达到续约的目的;如果租约不存在,那么返回续租失败的结果
服务剔除
如果Eureka Client在注册后,既没有续约,也没有下线(服务崩溃或者网络异常等原因),那么服务的状态就处于不可知的状态,不能保证能够从该服务实例中获取到回馈,所以需要服务剔除AbstractInstanceRegistry#evict方法定时清理这些不稳定的服务,该方法会批量将注册表中所有过期租约剔除。实现代码如下所示:
/*** Evicts everything in the instance registry that has expired, if expiry is enabled.* 如果启用了到期,则将实例注册表中已到期的所有内容逐出* @see com.netflix.eureka.lease.LeaseManager#evict()*/@Overridepublic void evict() {
evict(0l);}public void evict(long additionalLeaseMs) {
logger.debug("Running the evict task");// 检查是否启用了租约到期 // 自我保护机制如果出现该状态不允许剔除服务if (!isLeaseExpirationEnabled()) {
logger.debug("DS: lease expiration is currently disabled.");return;}//我们首先收集所有过期的物品,以随机顺序将其逐出。对于大型驱逐集,//如果不这样做,则可能会在自我保护开始之前先清除整个应用程序。通过将其随机化,//影响应均匀地分布在所有应用程序中。// 遍历注册表register,一次性获取所有的过期租约List<Lease<InstanceInfo>> expiredLeases = new ArrayList<>();for (Entry<String, Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>>> groupEntry : registry.entrySet()) {
Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> leaseMap = groupEntry.getValue();if (leaseMap != null) {
for (Entry<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> leaseEntry : leaseMap.entrySet()) {
Lease<InstanceInfo> lease = leaseEntry.getValue();if (lease.isExpired(additionalLeaseMs) && lease.getHolder() != null) {
expiredLeases.add(lease);}}}}//为了补偿GC暂停或本地时间漂移,我们需要使用当前注册表大小作为触发自我保存的基础。否则,我们将清除完整的注册表// 计算最大允许剔除的租约的数量,获取注册租约总数int registrySize = (int) getLocalRegistrySize();// 计算注册表租约的阈值,与自我保护相关int registrySizeThreshold = (int) (registrySize * serverConfig.getRenewalPercentThreshold());int evictionLimit = registrySize - registrySizeThreshold;// 计算剔除租约的数量int toEvict = Math.min(expiredLeases.size(), evictionLimit);if (toEvict > 0) {
logger.info("Evicting {} items (expired={}, evictionLimit={})", toEvict, expiredLeases.size(), evictionLimit);Random random = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis());// 逐个随机剔除for (int i = 0; i < toEvict; i++) {
// Pick a random item (Knuth shuffle algorithm)int next = i + random.nextInt(expiredLeases.size() - i);// 在指定列表中的指定位置交换元素。 (如果指定的位置相等,则调用此方法将使列表保持不变。Collections.swap(expiredLeases, i, next);Lease<InstanceInfo> lease = expiredLeases.get(i);String appName = lease.getHolder().getAppName();String id = lease.getHolder().getId();// EurekaMonitors 给定统计量增加计数器EXPIRED.increment();logger.warn("DS: Registry: expired lease for {}/{}", appName, id);// 逐个剔除internalCancel(appName, id, false);}}}
服务剔除将会遍历registry注册表,找出其中所有的过期租约,然后根据配置文件中续租百分比阀值和当前注册表的租约总数量计算出最大允许的剔除租约的数量(当前注册表中租约总数量减去当前注册表租约阀值),分批次剔除过期的服务实例租约。对过期的服务实例租约调用AbstractInstanceRegistry#internalCancel服务下线的方法将其从注册表中清除掉。服务剔除#evict方法中有很多限制,都是为了保证EurekaServer的可用性:
□ 自我保护时期不能进行服务剔除操作。
□ 过期操作是分批进行。
□ 服务剔除是随机逐个剔除,剔除均匀分布在所有应用中,防止在同一时间内同一服务集群中的服务全部过期被剔除,以致大量剔除发生时,在未进行自我保护前促使了程序的崩溃。
服务剔除是一个定时的任务,所以AbstractInstanceRegistry中定义了一个EvictionTask用于定时执行服务剔除,默认为60秒一次。服务剔除的定时任务一般在AbstractInstanceRegistry初始化结束后进行,按照执行频率evictionIntervalTimerInMs的设定,定时剔除过期的服务实例租约。自我保护机制主要在Eureka Client和Eureka Server之间存在网络分区的情况下发挥保护作用,在服务器端和客户端都有对应实现。假设在某种特定的情况下(如网络故障), Eureka Client和Eureka Server无法进行通信,此时Eureka Client无法向EurekaServer发起注册和续约请求,Eureka Server中就可能因注册表中的服务实例租约出现大量过期而面临被剔除的危险,然而此时的Eureka Client可能是处于健康状态的(可接受服务访问),如果直接将注册表中大量过期的服务实例租约剔除显然是不合理的。针对这种情况,Eureka设计了“自我保护机制”。在EurekaServer处,如果出现大量的服务实例过期被剔除的现象,那么该Server节点将进入自我保护模式,保护注册表中的信息不再被剔除,在通信稳定后再退出该模式;在Eureka Client处,如果向Eureka Server注册失败,将快速超时并尝试与其他的EurekaServer进行通信。“自我保护机制”的设计大大提高了Eureka的可用性。
服务下线
Eureka Client在应用销毁时,会向Eureka Server发送服务下线请求,清除注册表中关于本应用的租约,避免无效的服务调用。在服务剔除的过程中,也是通过服务下线的逻辑完成对单个服务实例过期租约的清除工作。服务下线的主要实现代码位于AbstractInstanceRegistry#internalCancel方法中,仅需要服务实例的服务名和服务实例id即可完成服务下线
/*** 取消实例的注册。通常,它在关闭客户端以通知服务器从流量中删除实例时由客户端调用。* </p>** @param appName the application name of the application.* @param id the unique identifier of the instance.* @param isReplication true if this is a replication event from other nodes, false* otherwise.* @return true if the instance was removed from the {@link AbstractInstanceRegistry} successfully, false otherwise.*/@Overridepublic boolean cancel(String appName, String id, boolean isReplication) {
return internalCancel(appName, id, isReplication);}/*** cancel(String, String, boolean)方法被PeerAwareInstanceRegistry覆盖,因此每个取消请求都复制到对等方。 但是,对于在远程对等方中视为有效取消的过期,这是不希望的,因此不会启动自我保存模式*/protected boolean internalCancel(String appName, String id, boolean isReplication) {
try {
// 获取锁,防止被其他线程进行修改read.lock();// 根据这是由于从其他eureka服务器进行复制还是由于eureka客户端启动的操作而增加给定统计信息的计数器// 调用EurekaMonitorsCANCEL.increment(isReplication);// 根据appName获取服务实例集群Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> gMap = registry.get(appName);Lease<InstanceInfo> leaseToCancel = null;// 移除服务实例的租约if (gMap != null) {
leaseToCancel = gMap.remove(id);}// 将服务实例信息添加到最近下线服务实例统计队列synchronized (recentCanceledQueue) {
recentCanceledQueue.add(new Pair<Long, String>(System.currentTimeMillis(), appName + "(" + id + ")"));}InstanceStatus instanceStatus = overriddenInstanceStatusMap.remove(id);if (instanceStatus != null) {
logger.debug("Removed instance id {} from the overridden map which has value {}", id, instanceStatus.name());}// 如果租约不存在返回falseif (leaseToCancel == null) {
CANCEL_NOT_FOUND.increment(isReplication);logger.warn("DS: Registry: cancel failed because Lease is not registered for: {}/{}", appName, id);return false;} else {
// 设置租约的下线时间leaseToCancel.cancel();InstanceInfo instanceInfo = leaseToCancel.getHolder();String vip = null;String svip = null;if (instanceInfo != null) {
instanceInfo.setActionType(ActionType.DELETED);// 添加最近租约变更记录的队列,标识ActionType为DELETED// 这将用于Eureka Client 增量式获取注册表信息recentlyChangedQueue.add(new RecentlyChangedItem(leaseToCancel));instanceInfo.setLastUpdatedTimestamp();vip = instanceInfo.getVIPAddress();svip = instanceInfo.getSecureVipAddress();}// 设置response缓存过期invalidateCache(appName, vip, svip);logger.info("Cancelled instance {}/{} (replication={})", appName, id, isReplication);// 下线成功return true;}} finally {
// 释放锁read.unlock();}}
internalCancel方法与register方法的行为过程很类似,首先通过registry根据服务名和服务实例id查询关于服务实例的租约Lease是否存在,统计最近请求下线的服务实例用于EurekaServer主页展示。如果租约不存在,返回下线失败;如果租约存在,从registry注册表中移除,设置租约的下线时间,同时在最近租约变更记录队列中添加新的下线记录,以用于EurekaClient的增量式获取注册表信息,最后设置repsonse缓存过期。internalCancel方法中同样通过读锁保证registry注册表中数据的一致性,避免脏读
集群同步
如果Eureka Server是通过集群的方式进行部署,那么为了维护整个集群中Eureka Server注册表数据的一致性,势必需要一个机制同步Eureka Server集群中的注册表数据。Eureka Server集群同步包含两个部分,一部分是EurekaServer在启动过程中从它的peer节点中拉取注册表信息,并将这些服务实例的信息注册到本地注册表中;另一部分是EurekaServer每次对本地注册表进行操作时,同时会将操作同步到它的peer节点中,达到集群注册表数据统一的目的
Eureka Server初始化本地注册表信息
在Eureka Server启动的过程中,会从它的peer节点中拉取注册表来初始化本地注册表,这部分主要通过PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl#syncUp方法完成,它将从可能存在的peer节点中,拉取peer节点中的注册表信息,并将其中的服务实例信息注册到本地注册表中
/*** Populates the registry information from a peer eureka node. This* operation fails over to other nodes until the list is exhausted if the* communication fails.*/@Overridepublic int syncUp() {
// 从临近的Peer中复制整个注册表// Copy entire entry from neighboring DS nodeint count = 0;// 如果获取不到,线程等待for (int i = 0; ((i < serverConfig.getRegistrySyncRetries()) && (count == 0)); i++) {
if (i > 0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(serverConfig.getRegistrySyncRetryWaitMs());} catch (InterruptedException e) {
logger.warn("Interrupted during registry transfer..");break;}}// 获取所有的服务实例Applications apps = eurekaClient.getApplications();for (Application app : apps.getRegisteredApplications()) {
for (InstanceInfo instance : app.getInstances()) {
try {
// 判断是否可注册,主要用于AWS环境下进行,若部署在其他的环境,直接返回trueif (isRegisterable(instance)) {
// 注册到自身的注册表中register(instance, instance.getLeaseInfo().getDurationInSecs(), true);count++;}} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.error("During DS init copy", t);}}}}return count;}
Eureka Server也是一个Eureka Client,在启动的时候也会进行DiscoveryClient的初始化,会从其对应的Eureka Server中拉取全量的注册表信息。在Eureka Server集群部署的情况下,Eureka Server从它的peer节点中拉取到注册表信息后,将遍历这个Applications,将所有的服务实例通过AbstractRegistry#register方法注册到自身注册表中。在初始化本地注册表时,Eureka Server并不会接受来自EurekaClient的通信请求(如注册、或者获取注册表信息等请求)。在同步注册表信息结束后会通过PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl#openForTraffic方法允许该Server接受流量
@Overridepublic void openForTraffic(ApplicationInfoManager applicationInfoManager, int count) {
// Renewals happen every 30 seconds and for a minute it should be a factor of 2.// 初始化自我保护机制统计参数this.expectedNumberOfRenewsPerMin = count * 2;this.numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold =(int) (this.expectedNumberOfRenewsPerMin * serverConfig.getRenewalPercentThreshold());logger.info("Got {} instances from neighboring DS node", count);logger.info("Renew threshold is: {}", numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold);this.startupTime = System.currentTimeMillis();// 如果同步的应用实例数量为0,将在一段时间内拒绝Client获取注册信息if (count > 0) {
this.peerInstancesTransferEmptyOnStartup = false;}DataCenterInfo.Name selfName = applicationInfoManager.getInfo().getDataCenterInfo().getName();boolean isAws = Name.Amazon == selfName;// 判断是否是AWS运行环境if (isAws && serverConfig.shouldPrimeAwsReplicaConnections()) {
logger.info("Priming AWS connections for all replicas..");primeAwsReplicas(applicationInfoManager);}logger.info("Changing status to UP");// 修改服务实例的状态为健康上线,可以接受流量applicationInfoManager.setInstanceStatus(InstanceStatus.UP);super.postInit();}
在Eureka Server中有一个StatusFilter过滤器,用于检查Eureka Server的状态,当Server的状态不为UP时,将拒绝所有的请求。在Client请求获取注册表信息时,Server会判断此时是否允许获取注册表中的信息。上述做法是为了避免EurekaServer在#syncUp方法中没有获取到任何服务实例信息时(Eureka Server集群部署的情况下), Eureka Server注册表中的信息影响到Eureka Client缓存的注册表中的信息。如果Eureka Server在#syncUp方法中没有获得任何的服务实例信息,它将把peerInstancesTransferEmptyOnStartup设置为true,这时该Eureka Server在WaitTimeInMsWhenSyncEmpty(可以通过eureka.server.wait-time-in-ms-when-sync-empty设置,默认是5分钟)时间后才能被Eureka Client访问获取注册表信息
Eureka Server之间注册表信息的同步复制
为了保证Eureka Server集群运行时注册表信息的一致性,每个Eureka Server在对本地注册表进行管理操作时,会将相应的操作同步到所有peer节点中。在PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl中,对Abstractinstanceregistry中的#register、#cancel和#renew等方法都添加了同步到peer节点的操作,使Server集群中注册表信息保持最终一致性,如下所示
@Overridepublic boolean cancel(final String appName, final String id,final boolean isReplication) {
if (super.cancel(appName, id, isReplication)) {
// 同步下线状态replicateToPeers(Action.Cancel, appName, id, null, null, isReplication);synchronized (lock) {
if (this.expectedNumberOfRenewsPerMin > 0) {
// Since the client wants to cancel it, reduce the threshold (1 for 30 seconds, 2 for a minute)this.expectedNumberOfRenewsPerMin = this.expectedNumberOfRenewsPerMin - 2;this.numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold =(int) (this.expectedNumberOfRenewsPerMin * serverConfig.getRenewalPercentThreshold());}}return true;}return false;}/*** Registers the information about the {@link InstanceInfo} and replicates* this information to all peer eureka nodes. If this is replication event* from other replica nodes then it is not replicated.** @param info* the {@link InstanceInfo} to be registered and replicated.* @param isReplication* true if this is a replication event from other replica nodes,* false otherwise.*/@Overridepublic void register(final InstanceInfo info, final boolean isReplication) {
int leaseDuration = Lease.DEFAULT_DURATION_IN_SECS;if (info.getLeaseInfo() != null && info.getLeaseInfo().getDurationInSecs() > 0) {
leaseDuration = info.getLeaseInfo().getDurationInSecs();}super.register(info, leaseDuration, isReplication);// 同步注册状态replicateToPeers(Action.Register, info.getAppName(), info.getId(), info, null, isReplication);}/** (non-Javadoc)** @see com.netflix.eureka.registry.InstanceRegistry#renew(java.lang.String,* java.lang.String, long, boolean)*/public boolean renew(final String appName, final String id, final boolean isReplication) {
if (super.renew(appName, id, isReplication)) {
// 同步续约状态replicateToPeers(Action.Heartbeat, appName, id, null, null, isReplication);return true;}return false;}private void replicateToPeers(Action action, String appName, String id,InstanceInfo info /* optional */,InstanceStatus newStatus /* optional */, boolean isReplication) {
Stopwatch tracer = action.getTimer().start();try {
if (isReplication) {
numberOfReplicationsLastMin.increment();}// If it is a replication already, do not replicate again as this will create a poison replication// 如果peer集群为空,或者这本来就是复制操作,那么就不再复制,防止造成循环复制if (peerEurekaNodes == Collections.EMPTY_LIST || isReplication) {
return;}// 向peer 集群的每一个peer进行同步for (final PeerEurekaNode node : peerEurekaNodes.getPeerEurekaNodes()) {
// If the url represents this host, do not replicate to yourself.// 如果peer节点是自身的话,不进行同步复制if (peerEurekaNodes.isThisMyUrl(node.getServiceUrl())) {
continue;}// 根据Action调用不同的同步请求replicateInstanceActionsToPeers(action, appName, id, info, newStatus, node);}} finally {
tracer.stop();}}/*** Replicates all instance changes to peer eureka nodes except for* replication traffic to this node.* 根据action的不同,调用PeerEurekaNode的不同方法进行同步复制* 将所有实例更改复制到对等eureka节点,但复制到该节点的流量除外* Action是一个枚举内部类 包含 Heartbeat,Refister,Cancel,StatusUpdate,DeleteStatusOverride*/private void replicateInstanceActionsToPeers(Action action, String appName,String id, InstanceInfo info, InstanceStatus newStatus,PeerEurekaNode node) {
try {
InstanceInfo infoFromRegistry = null;CurrentRequestVersion.set(Version.V2);switch (action) {
case Cancel:// 同步下线node.cancel(appName, id);break;case Heartbeat:InstanceStatus overriddenStatus = overriddenInstanceStatusMap.get(id);infoFromRegistry = getInstanceByAppAndId(appName, id, false);// 同步心跳node.heartbeat(appName, id, infoFromRegistry, overriddenStatus, false);break;case Register:// 同步注册node.register(info);break;case StatusUpdate:infoFromRegistry = getInstanceByAppAndId(appName, id, false); // 同步状态更新node.statusUpdate(appName, id, newStatus, infoFromRegistry);break;case DeleteStatusOverride:infoFromRegistry = getInstanceByAppAndId(appName, id, false);node.deleteStatusOverride(appName, id, infoFromRegistry);break;}} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.error("Cannot replicate information to {} for action {}", node.getServiceUrl(), action.name(), t);}}
PeerEurekaNode中的每一个同步复制都是通过批任务流的方式进行操作,同一时间段内相同服务实例的相同操作将使用相同的任务编号,在进行同步复制的时候根据任务编号合并操作,减少同步操作的数量和网络消耗,但是同时也造成同步复制的延时性,不满足CAP中的C(强一致性)。通过Eureka Server在启动过程中初始化本地注册表信息和Eureka Server集群间的同步复制操作,最终达到了集群中Eureka Server注册表信息一致的目的
获取注册表中服务实例信息
Eureka Server中获取注册表的服务实例信息主要通过两个方法实现:AbstractInstanceRegistry .getApplicationsFromMultipleRegions()从多地区获取全量注册表数据,AbstractInstanceRegistry.getApplicationDeltasFromMultipleRegions()从多地区获取增量式注册表数据。
getApplicationsFromMultipleRegions获取全量注册表数据
public Applications getApplicationsFromMultipleRegions(String[] remoteRegions) {
boolean includeRemoteRegion = null != remoteRegions && remoteRegions.length != 0;logger.debug("Fetching applications registry with remote regions: {}, Regions argument {}",includeRemoteRegion, remoteRegions);if (includeRemoteRegion) {
GET_ALL_WITH_REMOTE_REGIONS_CACHE_MISS.increment();} else {
GET_ALL_CACHE_MISS.increment();}Applications apps = new Applications();apps.setVersion(1L);// 从本地registry获取所有的服务实例信息InstanceInfofor (Entry<String, Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>>> entry : registry.entrySet()) {
Application app = null;if (entry.getValue() != null) {
for (Entry<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> stringLeaseEntry : entry.getValue().entrySet()) {
Lease<InstanceInfo> lease = stringLeaseEntry.getValue();if (app == null) {
app = new Application(lease.getHolder().getAppName());}app.addInstance(decorateInstanceInfo(lease));}}if (app != null) {
apps.addApplication(app);}}if (includeRemoteRegion) {
// 获取远程Region中的Eureka Server中的注册表信息for (String remoteRegion : remoteRegions) {
RemoteRegionRegistry remoteRegistry = regionNameVSRemoteRegistry.get(remoteRegion);if (null != remoteRegistry) {
Applications remoteApps = remoteRegistry.getApplications();for (Application application : remoteApps.getRegisteredApplications()) {
if (shouldFetchFromRemoteRegistry(application.getName(), remoteRegion)) {
logger.info("Application {} fetched from the remote region {}",application.getName(), remoteRegion);Application appInstanceTillNow = apps.getRegisteredApplications(application.getName());if (appInstanceTillNow == null) {
appInstanceTillNow = new Application(application.getName());apps.addApplication(appInstanceTillNow);}for (InstanceInfo instanceInfo : application.getInstances()) {
appInstanceTillNow.addInstance(instanceInfo);}} else {
logger.debug("Application {} not fetched from the remote region {} as there exists a "+ "whitelist and this app is not in the whitelist.",application.getName(), remoteRegion);}}} else {
logger.warn("No remote registry available for the remote region {}", remoteRegion);}}}apps.setAppsHashCode(apps.getReconcileHashCode());return apps;}它首先会将本地注册表registry中的所有服务实例信息提取出来封装到Applications中,再根据是否需要拉取远程Region中的注册表信息,将远程Region的Eureka Server注册表中的服务实例信息添加到Applications中。最后将封装了全量注册表信息的Applications返回给Client
getApplicationDeltasFromMultipleRegions从多地区获取增量式注册表数据。
getApplicationDeltasFromMultipleRegions方法将会从多个地区中获取增量式注册表信息,并封装成Applications返回,实现代码如下所示
public Applications getApplicationDeltasFromMultipleRegions(String[] remoteRegions) {
if (null == remoteRegions) {
remoteRegions = allKnownRemoteRegions; // null means all remote regions.}boolean includeRemoteRegion = remoteRegions.length != 0;if (includeRemoteRegion) {
GET_ALL_WITH_REMOTE_REGIONS_CACHE_MISS_DELTA.increment();} else {
GET_ALL_CACHE_MISS_DELTA.increment();}Applications apps = new Applications();apps.setVersion(responseCache.getVersionDeltaWithRegions().get());Map<String, Application> applicationInstancesMap = new HashMap<String, Application>();try {
// 开启写锁write.lock();// 遍历recentlyChangedQueue队列获取最近变化的服务实例信息InstanceInfoIterator<RecentlyChangedItem> iter = this.recentlyChangedQueue.iterator();logger.debug("The number of elements in the delta queue is :{}", this.recentlyChangedQueue.size());while (iter.hasNext()) {
Lease<InstanceInfo> lease = iter.next().getLeaseInfo();InstanceInfo instanceInfo = lease.getHolder();logger.debug("The instance id {} is found with status {} and actiontype {}",instanceInfo.getId(), instanceInfo.getStatus().name(), instanceInfo.getActionType().name());Application app = applicationInstancesMap.get(instanceInfo.getAppName());if (app == null) {
app = new Application(instanceInfo.getAppName());applicationInstancesMap.put(instanceInfo.getAppName(), app);apps.addApplication(app);}app.addInstance(decorateInstanceInfo(lease));}if (includeRemoteRegion) {
// 获取远程Region中的Eureka Server的增量式注册表信息for (String remoteRegion : remoteRegions) {
RemoteRegionRegistry remoteRegistry = regionNameVSRemoteRegistry.get(remoteRegion);if (null != remoteRegistry) {
Applications remoteAppsDelta = remoteRegistry.getApplicationDeltas();if (null != remoteAppsDelta) {
for (Application application : remoteAppsDelta.getRegisteredApplications()) {
if (shouldFetchFromRemoteRegistry(application.getName(), remoteRegion)) {
Application appInstanceTillNow =apps.getRegisteredApplications(application.getName());if (appInstanceTillNow == null) {
appInstanceTillNow = new Application(application.getName());apps.addApplication(appInstanceTillNow);}for (InstanceInfo instanceInfo : application.getInstances()) {
appInstanceTillNow.addInstance(instanceInfo);}}}}}}}Applications allApps = getApplicationsFromMultipleRegions(remoteRegions);// 计算应用集合一致性哈希码,用以在Eureka Client拉取时进行对比apps.setAppsHashCode(allApps.getReconcileHashCode());return apps;} finally {
write.unlock();}}
获取增量式注册表信息将会从recentlyChangedQueue队列中获取最近变化的服务实例信息。recentlyChangedQueue队列中统计了近3分钟内进行注册、修改和剔除的服务实例信息,在服务注册AbstractInstanceRegistry.registry()、接受心跳请求AbstractInstanceRegistry.renew()和服务下线AbstractInstanceRegistry.internalCancel()等方法中均可见到recentlyChangedQueue队列对这些服务实例进行登记,用于记录增量式注册表信息。getApplicationsFromMultipleRegions()方法同样提供了从远程Region的Eureka Server获取增量式注册表信息的能力
Eureka和ZooKeeper
著名的CAP理论指出,一个分布式系统不可能同时满足C(一致性)、A(可用性)和P(分区容错性)。由于分区容错性在是分布式系统中必须要保证的,因此我们只能在A和C之间进行权衡。
ZooKeeper保证CP
当向注册中心查询服务列表时,我们可以容忍注册中心返回的是几分钟以前的注册信息,但不能接受服务直接down掉不可用。也就是说,服务注册功能对可用性的要求要高于一致性。但是ZooKeeper会出现这样一种情况,当Master节点因为网络故障与其他节点失去联系时,剩余节点会重新进行leader选举。问题在于,选举leader的时间太长,30 ~ 120s,且选举期间整个ZooKeeper集群都是不可用的,这就导致在选举期间注册服务瘫痪。在云部署的环境下,因网络问题使得ZooKeeper集群失去Master节点是较大概率会发生的事,虽然服务能够最终恢复,但是漫长的选举时间导致的注册长期不可用是不能容忍的。
Eureka保证AP
Eureka在设计时就优先保证可用性。Eureka各个节点都是平等的,几个节点挂掉不会影响正常节点的工作,剩余的节点依然可以提供注册和查询服务。而Eureka的客户端在向某个Eureka注册或时如果发现连接失败,则会自动切换至其它节点,只要有一台Eureka还在,就能保证注册服务可用(保证可用性),只不过查到的信息可能不是最新的(不保证强一致性)。
参考:https://www.jianshu.com/p/6a3db6939fb0