目录
1,最短寻道时间优先算法(SSTF)
2,扫描算法(又称电梯算法)
1,最短寻道时间优先算法(SSTF)
- SSTF问题描述:SSTF算法选择调度处理的磁道是与当前磁头所在磁道距离最近的磁道,以使每次的寻找时间最短。当然,总是选择最小寻找时间并不能保证平均寻找时间最小,但是能提供比FCFS算法更好的性能。这种算法会产生“饥饿”现象。
-
1、算法思想:优先选择距当前磁头最近的访问请求进行服务,主要考虑寻道优先。
2、优点:改善了磁盘平均服务时间。
3、缺点:造成某些访问请求长期等待得不到服务。
-
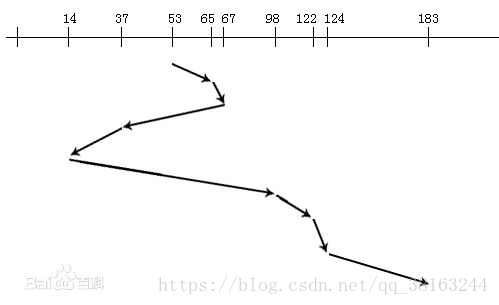
本算法是对输入的磁道首先进行非递减排序,然后判断当前磁头所在的磁道是否在将要寻找的磁道中,分别进行最短寻道时间计算。(如下图示,表示SSTF示意图)
- 代码实现:
//最短寻道时间优先SSTF
#include "pch.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//快速排序
int Partition(int *p, int low, int high)
{int i = low, j = high, pivot = p[low];while (i < j){while (i < j&&p[j] >= pivot){j--;}if (i < j){p[i] = p[j];i++;}while (i < j&&p[i] <= pivot){i++;}if (i < j){p[j] = p[i];j--;}}p[i] = pivot;return i;
}
void QuickSort(int *q, int left, int right)
{if (left < right){int pivotpos = Partition(q, left, right);QuickSort(q, left, pivotpos - 1);QuickSort(q, pivotpos + 1, right);}}
int main()
{int count = 0;//输入磁盘请求的个数int currentStair;//当前所在的磁道int n;int temp_1, temp_2;int size = 0;//步数计数变量int temp_3, temp_4;cout << "请输入要寻到的数量:" << endl;cin >> count;n = count;int *arr = new int[count];cout << "请输入要寻得磁道:" << endl;for (int i = 0; i < count; i++){cin >> arr[i];//输入楼梯数}cout << "please input currentstars:" << endl;cin >> currentStair;QuickSort(arr, 0, count - 1);for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)//当前磁道在要寻磁道中{if (currentStair == arr[i]) {currentStair = arr[i];temp_1 = i - 1;temp_2 = temp_1 + 1;while (temp_1 >= 0 && temp_2 < count){if (abs(currentStair - arr[temp_1]) < abs(arr[temp_2] - currentStair)){size += abs(currentStair - arr[temp_1]);currentStair = arr[temp_1];if (temp_1 > 0)temp_1 -= 1;if (currentStair == arr[temp_1]){while (temp_2 < count){size += abs(arr[temp_2] - currentStair);currentStair = arr[temp_2];temp_2++;}}}else {size += abs(arr[temp_2] - currentStair);if (temp_2 < count)temp_2 += 1;if (currentStair == arr[temp_2]){while (temp_1 > 0){size += abs(arr[temp_1] - currentStair);currentStair = arr[temp_1];temp_1--;}}}}}}for (int h = 0; h < count; h++)//当前所在的位置不在要寻的磁道中{if (currentStair > arr[h - 1] && currentStair < arr[h])//定位当前的位置{temp_3 = h - 1;temp_4 = h;while (temp_3 >= 0 && temp_4 < count){if (abs(currentStair - arr[temp_3]) < abs(arr[temp_4] - currentStair)){size += abs(currentStair - arr[temp_3]);currentStair = arr[temp_3];if (temp_3 > 0)temp_3 -= 1;if (currentStair == arr[temp_3]){while (temp_4 < count){size += arr[temp_4] - currentStair;currentStair = arr[temp_4];temp_4++;}}}else {size += abs(arr[temp_4] - currentStair);currentStair = arr[temp_4];if (temp_4 < count)temp_4 += 1;if (currentStair == arr[temp_4]){while (temp_3 > 0){size += arr[temp_3] - currentStair;currentStair = arr[temp_3];temp_3--;}}}}}elseif (currentStair < arr[0]){int i = 0;while (i < count){size += abs(arr[i] - currentStair);currentStair = arr[i];i++;}}elseif (currentStair > arr[count - 1]){int j = count - 1;while (j > 0){size += abs(arr[j] - currentStair);currentStair = arr[j];j--;}}}int average = size / count;cout << "最少寻磁道数是:"<<size<<"平均寻磁道数是:"<<average<< endl;
}2,扫描算法(又称电梯算法)
- 扫描算法问题描述:SCAN算法在磁头当前移动方向上选择与当前磁头所在磁道距离最近的请求作为下一次服务的对象。由于磁头移动规律与电梯运行相似,故又称为电梯调度算法。SCAN算法对最近扫描过的区域不公平,因此,它在访问局部性方面不如FCFS算法和SSTF算法好。
- 算法思想:当设备无访问请求时,磁头不动;当有访问请求时,磁头按一个方向移动,在移 [2] 动过程中对遇到的访问 请 求 进行服务,然后判断该方向上是否还有访问请求,如果有则继续扫描;否则改变移动方向,并为经过的访问请求服务,如此反复 。
- 优点:克服了最短寻道优先的缺点,既考虑了距离,同时又考虑了方向。(如下图表示SCAN图示)
- 代码实现:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test_louti {
//本算法我假设楼梯最大到200层,public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println("please input your scan from 1 to 200:");Scanner input =new Scanner(System.in);int []arr=new int[200];//200楼电梯System.out.println("请输入你要输入的楼层数:");int number=input.nextInt();//number记录当前所在楼梯int b=0;System.out.println("请输入楼梯:");for(int i=0;i<=200;i++){if(b<number){int num=input.nextInt();arr[num]=num;//记住楼梯,从小到大b++;i++;}if(b==number)break;}System.out.println("请输入当前楼梯号码:");int currentScan=input.nextInt();//当前楼梯int i=currentScan,team=0,j=0,a=currentScan;arr[currentScan]=currentScan;while(i<200)//i记住当前判断的楼梯号码{if(arr[i]!=0){team+=(arr[i]-arr[currentScan]);currentScan=i;j=i;//记住最后的楼梯号码}i+=1;}//下半层while(a>0){if(arr[a]!=0){team+=Math.abs((arr[a]-arr[j]));j=a; }a-=1;}System.out.println("总的移动量是:"+team);}}